2025-12-17 中国科学院(CAS)
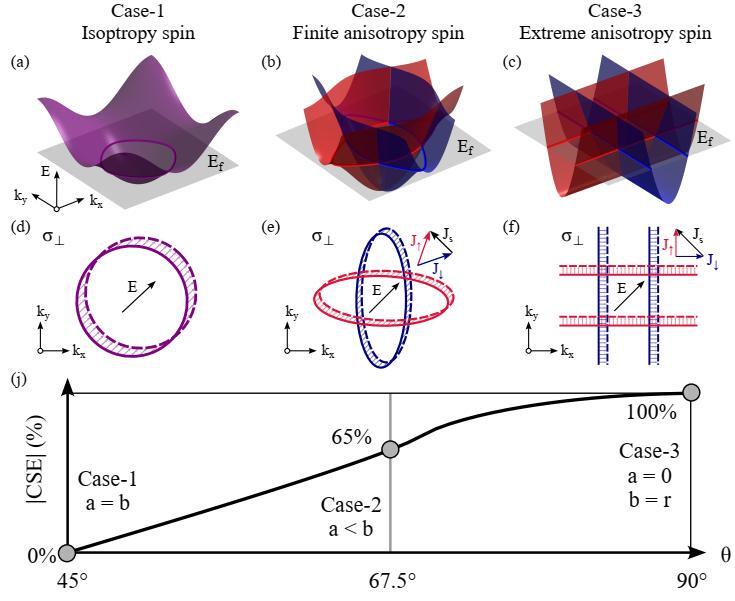
Effective model of altermagnets with different spin-splitting anisotropy (Image by IMR)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202512/t20251218_1137812.shtml
- https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/bf1n-sxdl
オルタマグネットの波面平坦フェルミ面が最大の電荷-スピン変換を可能にする -Wave Flat Fermi Surface in Altermagnets Enables Maximum Charge-to-Spin Conversion
Junwen Lai, Tianye Yu, Peitao Liu,, Long Liu, Guozhong Xing, Xing-Qiu Chen, and Yan Sun
Physical Review Letters Published 16 December, 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/bf1n-sxdl
Abstract
Altermagnets combine antiferromagnetic order with ferromagnetlike spin splitting, a duality that unlocks ultrafast spin-dependent responses. This unique property creates unprecedented opportunities for spin-current generation, overcoming the intrinsic limitations of conventional spin-transfer and spin-orbit torque approaches in magnetic memory technologies. Here, we establish a fundamental relationship between Fermi surface geometry and time-reversal-odd (-odd) spin currents in altermagnets through combined model analysis and first-principles calculations. We demonstrate that a -wave altermagnet with a flat Fermi surface can achieve a theoretical upper limit of charge-to-spin conversion efficiency (CSE) of 100%. This mechanism is realized in the newly discovered room-temperature altermagnetic metal KV2Se2O, which exhibits a CSE of ∼78% at the charge neutrality point—nearly double that of RuO2, setting a new record for -odd CSE. Under electron doping, this efficiency further increases to ∼98%, approaching the theoretical limit. Our Letter advances the fundamental understanding of -odd spin currents via Fermi surface geometry engineering and provides key insights for developing next-generation altermagnet-based memory devices.


 個人アグスタA109E(回転翼航空機)の重大インシデント[航空機の装置故障による操縦障害](茨城県結城郡八千代町上空、令和6年7月28日発生)](https://tiisys.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/スクリーンショット-2025-12-18-170406-500x179.png)
