2025-12-15 名古屋工業大学,科学技術振興機構
<関連情報>
- https://www.nitech.ac.jp/news/press/2025/13506.html
- https://www.nitech.ac.jp/mt_files/251215press_shibata.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-67299-y
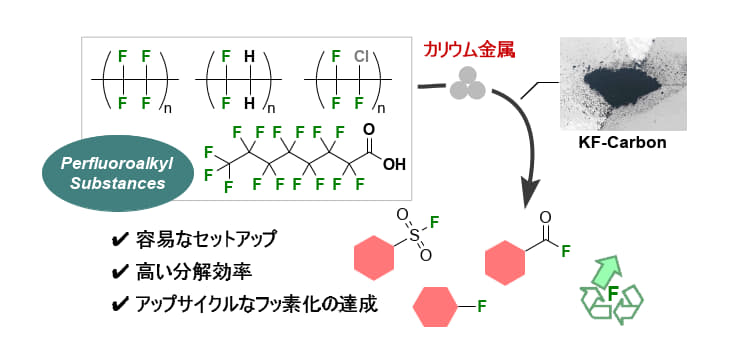
メカノケミカルプロセスによるPTFEおよびPVDFのフッ素化学物質へのアップサイクル Upcycling of PTFE and PVDF to fluorochemicals through mechanochemical process
Masashi Hattori,Tatsuki Kiyono,Zhengyu Zhao,Masahiro Higashi,Moe Fujishiro,Yosuke Kishikawa,Jorge Escorihuela & Norio Shibata
Nature Communications Published:11 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67299-y
We are providing an unedited version of this manuscript to give early access to its findings. Before final publication, the manuscript will undergo further editing. Please note there may be errors present which affect the content, and all legal disclaimers apply.
Abstract
The polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) industry has undergone significant expansion since the 1940s. However, the waste from PTFE products at the conclusion of their life cycle has rarely been subjected to recycling processes due to PTFE’s highly crystalline structure and high melting point. Despite considerable efforts, current approaches remain insufficient for the reuse of PTFE products. Herein, we present a method for upcycling of PTFE as a fluorinating reagent through reductive mechanochemical process mediated by potassium metal. This process efficiently degrades PTFE, including the commercial PTFE thread seal tape, within a short reaction time of 1 h at an ambient temperature to KFPTFE-Carbon. The KFPTFE-Carbon, consisting of potassium fluoride and carbon black (spectroscopic techniques suggest the carbon black possesses characteristics of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) after the washing process), can be directly used in fluorination reactions, yielding fluorochemicals in moderate to excellent results. The process can be extended to the destruction of a series of multiple per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), resulting in a high recovery ratio of fluorine content.



