2025-05-20 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202505/t20250520_1044147.shtml
- https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.1038/s44318-025-00462-9
グルタレドキシンWG1によるGタンパク質オリゴマー化とシグナル伝達の酸化還元制御がイネの粒度を制御する Redox regulation of G protein oligomerization and signaling by the glutaredoxin WG1 controls grain size in rice
Lijie Liu, Jianqin Hao, Ke Huang, Penggen Duan, Baolan Zhang, Zhihai Chi, Xiaohong Yao, and Yunhai Li
The EMBO Journal Published:19 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-025-00462-9
Abstract
Grain size is an important agronomic trait and influences both grain yield and quality in crops. The atypical heterotrimeric Gγ protein subunit GS3 is a central regulator of grain length in rice, and the loss-of-function allele of its corresponding gene has been widely utilized by breeders to improve grain length in rice. Here we report that the CC-type glutaredoxin WG1/OsGRX8 has disulfide oxidoreductase activity and regulates redox state of GS3, thereby determining grain length in rice. GS3 can form dimers and oligomers by intermolecular disulfide bonds, and the cysteine-rich C-terminal region of GS3 is predominantly required for its oligomerization. The oligomerization of GS3 alleviates its inhibitory effect on the interaction between RGB1 and DEP1/GGC2, resulting in an increase in grain length. WG1 interacts with GS3 and reduces the oligomerization of GS3 through redox mechanisms, which causes a decrease in grain length. Genetic analyses support WG1 and GS3 function in a common pathway to control grain length. Thus, our findings reveal a previously unrecognized mechanism, in which redox regulation of a Gγ subunit by a glutaredoxin controls grain length, opening a novel perspective for G protein signaling regulation.
Synopsis
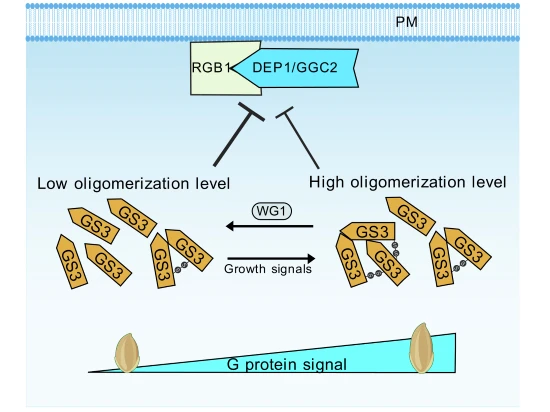
GS3 is an atypical heterotrimeric G protein Gγ subunit and represents a popular target for improving grain length in rice breeding. This study demonstrates that the glutaredoxin WG1/OsGRX8 interacts with GS3, reducing this oligomerization and grain length.
- GS3 can form oligomers through intermolecular disulfide bonds.
- WG1 interacts with GS3 to reduce its oligomerization level.
- The oligomerization of GS3 decreases its inhibitory effect on the RGB1-DEP1/GGC2 interaction, thereby increasing grain length.