2025-03-12 京都大学
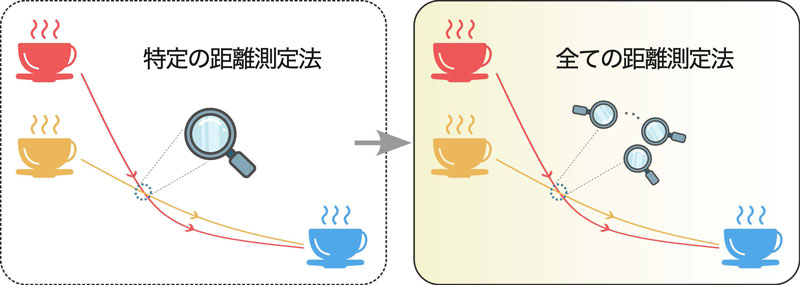
(左)従来のペンバ効果の理論では、全変動距離やカルバック・ライブラー発散など、特定の距離測定法を用いて緩和速度を定量化する。(右)本研究では、熱的マジョライゼーションに基づくペンバ効果を提案し、すべての距離測定法を同時に活用して緩和の傾向を包括的に評価する新たな枠組みを構築する。
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-03-11-0
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-03/web_2503_Vu-768fe7f7109685a6035fd7031390d2c6.pdf
- https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.107101
熱変成ムペンバ効果 Thermomajorization Mpemba Effect
Tan Van Vu and Hisao Hayakawa
Physical Review Letters Published: 10 March, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.107101
Abstract
The Mpemba effect is a counterintuitive physical phenomenon where a hot system cools faster than a warm one. In recent years, theoretical analyses of the Mpemba effect have been developed for microscopic systems and experimentally verified. However, the conventional theory relies on a specific choice of distance measure to quantify relaxation speed, leading to several theoretical ambiguities. In this Letter, we derive a rigorous quantification of the Mpemba effect based on thermomajorization theory, referred to as the thermomajorization Mpemba effect. This approach resolves all existing ambiguities and provides a unification of the conventional Mpemba effect across all monotone measures. Furthermore, we demonstrate the generality of the thermomajorization Mpemba effect for Markovian dynamics, rigorously proving that it can occur in any temperature regime with fixed energy levels.