2024-12-12 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2024/12/12/technique-forecast-where-next-big-quake-will-start
- https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article/52/12/917/649016/Rupture-direction-of-paleoearthquakes-on-the?searchresult=1
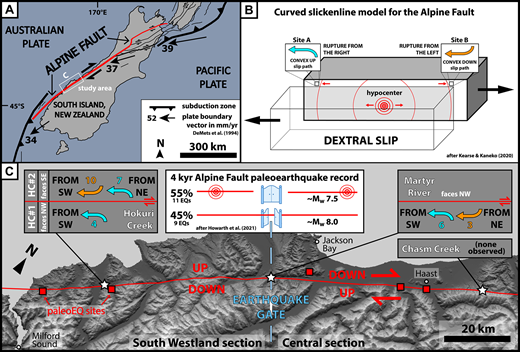
ニュージーランドのアルパイン断層で発生した古地震の破壊方向 Rupture direction of paleoearthquakes on the Alpine Fault, New Zealand, as recorded by curved slickenlines
Nicolas C. Barth;Jesse R. Kearse;Timothy A. Little;Russ J. Van Dissen
Geology Published October 07, 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1130/G52543.1
Abstract
We observed and further exhumed curved slickenlines on fault planes associated with paleo-surface rupture of the Alpine Fault, New Zealand’s ∼30 mm/yr continental transform plate boundary. Dynamic rupture modeling indicates that the geometry of such curvature provides a record of past earthquake rupture directions. We focused our efforts on three sites that span a region known to variably halt or allow passage of past earthquakes (an “earthquake gate”) to contribute rupture direction constraints to the fault’s spatiotemporally rich paleoseismic record. At Hokuri Creek and Martyr River, we observed both convex-up and convex-down curved slickenlines on and adjacent to principal slip surfaces, indicating past ruptures from both the northeast and southwest of these locations. At Martyr River, relationships suggest that the most recent event (inferred to correlate to 1717 CE) ruptured from the southwest. Our results demonstrate the utility of curved slickenlines as a valuable new paleoseismological tool for determining past rupture directions, applicable to surface-rupturing faults globally.