2024-11-20 デラウェア大学 (UD)
<関連情報>
- https://www.udel.edu/udaily/2024/november/ecosystem-safety-chemical-upcycling-toxic-tires/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44286-024-00110-9
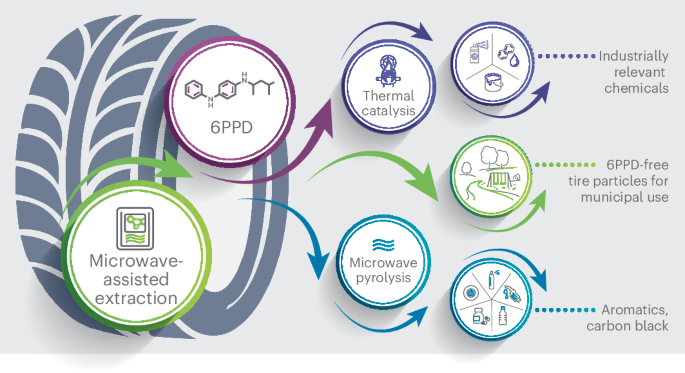
6PPDとアップサイクルによる使用済みタイヤの汚染除去 End-of-life tire decontamination from 6PPD and upcycling
Sean Najmi,Pooja Bhalode,Montgomery Baker-Fales,Brandon C. Vance,Esun Selvam,Kewei Yu,Weiqing Zheng & Dionisios G. Vlachos
Nature Chemical Engineering Published:29 August 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44286-024-00110-9
Abstract
N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD) is a ubiquitous rubber antioxidant and antiozonant that extends the lifetime of common rubber products, such as those found in tires. It transforms into a quinone derivative following certain environmental conditions. 6PPD and the quinone can leach into the environment and cause severe morbidity to aquatic life at diminutive concentrations, with health effects on humans still not fully understood. With legislation on the horizon to ban 6PPD entirely, developing effective methods for its removal and conversion to safe compounds is essential. Here we show that 6PPD survives microwave-assisted pyrolysis and escapes in the oil product, rendering decontamination essential. We introduce a decontamination strategy that removes 6PPD from end-of-life tires before it enters the broader ecosystem. We demonstrate the catalytic upgrade of 6PPD to safe chemicals and the valorization of crumb rubber to aromatics and carbon black using microwave-assisted pyrolysis.



