2024-04-15 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-024-01152-w
直交伸縮型量子ドット発光ダイオード Intrinsically stretchable quantum dot light-emitting diodes
Dong Chan Kim,Hyojin Seung,Jisu Yoo,Junhee Kim,Hyeon Hwa Song,Ji Su Kim,Yunho Kim,Kyunghoon Lee,Changsoon Choi,Dongjun Jung,Chansul Park,Hyeonjun Heo,Jiwoong Yang,Taeghwan Hyeon,Moon Kee Choi & Dae-Hyeong Kim
Nature Electronics Published:15 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01152-w
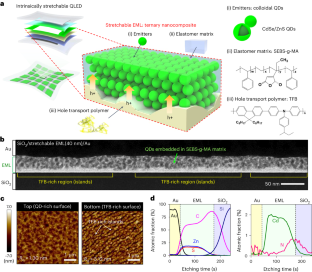
Abstract
Stretchable displays that can change their shape and size under strain could be used to create displays with unconventional form factors. However, intrinsically stretchable light-emitting devices have poor luminous performance, such as low brightness. Here we show that intrinsically stretchable quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) can be made using a mechanically soft and stretchable emissive layer consisting of a ternary nanocomposite of colloidal quantum dots, an elastomeric polymer and a charge transport polymer. The light-emitting layer maintains a nearly constant interparticle distance even under 50% strain, ensuring reliable operation of the QLED under stretching. The polymer-rich charge transport region at the bottom of the nanocomposite functions as a hole transport pathway to the embedded quantum dots. The QLEDs exhibit a turn-on voltage of 3.2 V and a maximum luminance of 15,170 cd m−2 at 6.2 V without loss of brightness, even when under 50% strain, and can be used to make stretchable full-colour passive-matrix QLED arrays.



