2025-12-23 アメリカ合衆国・コネティカット大学 (UCONN)
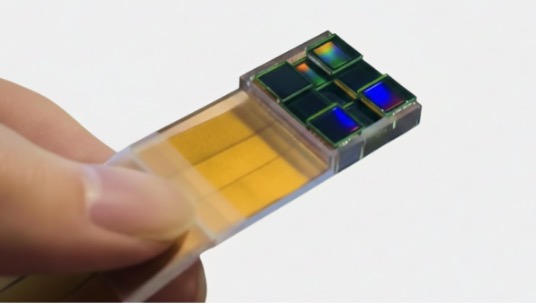
Professor Guoan Zheng’s lab developed a new image sensor that achieves optical super-resolution without lenses. Inspired by the telescope array that captured the first black hole image, the device uses multiple sensors working in concert, computationally merging their observations to see finer details (Contributed photo).
<関連情報>
- https://today.uconn.edu/2025/12/new-image-sensor-breaks-optical-limits/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-65661-8
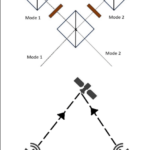
マルチスケール開口合成イメージャー Multiscale aperture synthesis imager
Ruihai Wang,Qianhao Zhao,Tianbo Wang,Mitchell Modarelli,Peter Vouras,Zikun Ma,Zhixuan Hong,Kazunori Hoshino,David Brady & Guoan Zheng
Nature Communications Published:26 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-65661-8
Abstract
Synthetic aperture imaging has enabled breakthrough observations from radar to astronomy. However, optical implementation remains challenging due to stringent wavefield synchronization requirements among multiple receivers. Here we present the multiscale aperture synthesis imager (MASI), which utilizes parallelism to break complex optical challenges into tractable sub-problems. MASI employs a distributed array of coded sensors that operate independently yet coherently to surpass the diffraction limit of single receiver. It combines the propagated wavefields from individual sensors through a computational phase synchronization scheme, eliminating the need for overlapping measurement regions to establish phase coherence. Light diffraction in MASI naturally expands the imaging field, generating phase-contrast visualizations that are substantially larger than sensor dimensions. Without using lenses, MASI resolves sub-micron features at ultralong working distances and reconstructs 3D shapes over centimeter-scale fields. MASI transforms the intractable optical synchronization problem into a computational one, enabling practical deployment of scalable synthetic aperture systems at optical wavelengths.