2026-01-07 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/cas-in-media/202601/t20260107_1145348.shtml
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.202502032
H2S電気分解によるH 2生成用の高効率で耐久性のある一体型チェーンメイル電極 Highly Effective and Durable Integrated-Chainmail Electrode for H2 Production through H2S Electrolysis
Mo Zhang, Zuochao Wang, Liumo Jiang, Xin Bo, Xiaoju Cui, Dehui Deng
Angewandte Chemie International Edition Published: 13 February 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202502032
Graphical Abstract
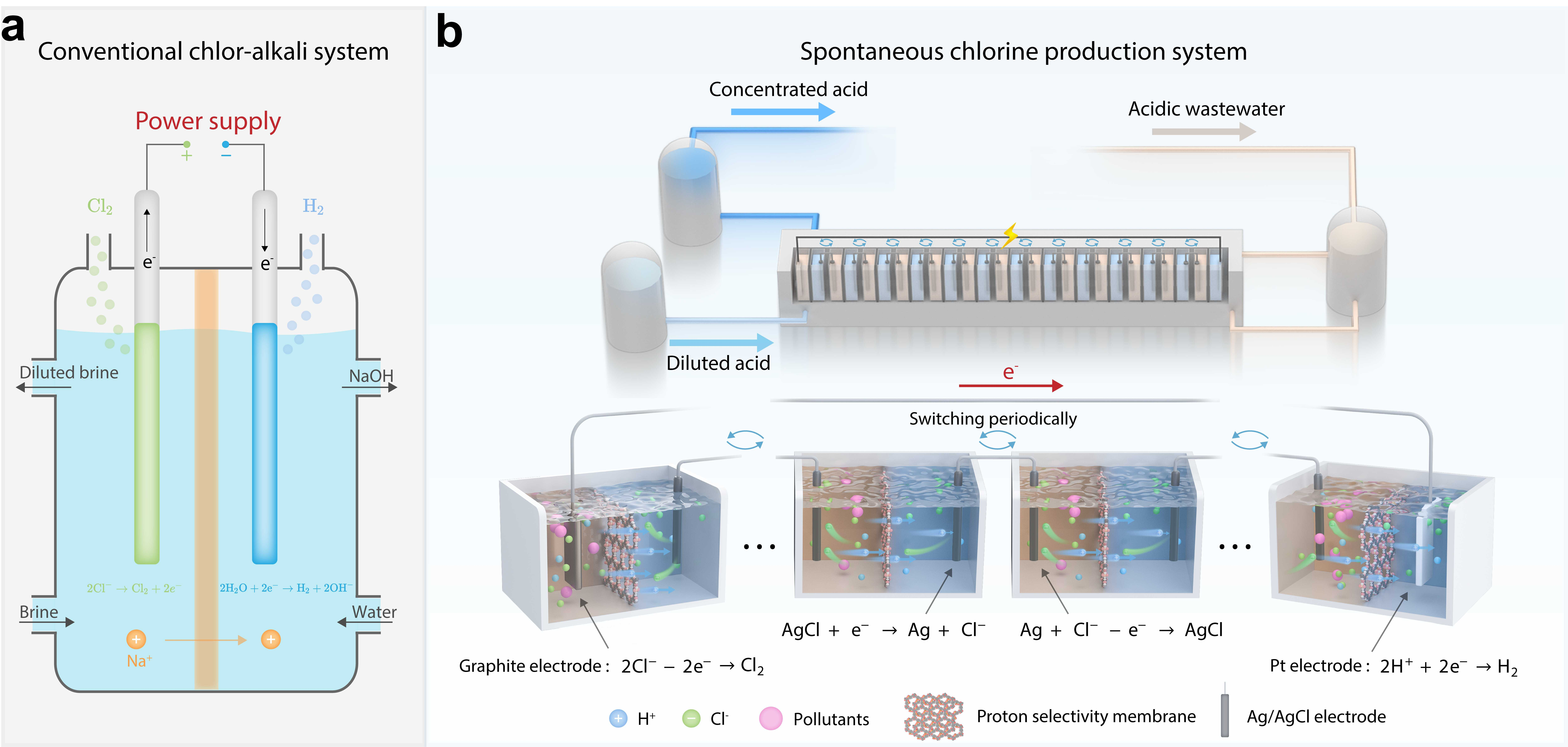
A robust integrated electrode that features a dual-level chainmail structure with graphene encapsulating nickel foam is developed to enhance H2S electrolysis for green hydrogen production. The unique integrated-chainmail structure significantly improves both the activity and stability of the nickel foam. This chainmail electrodes realizes efficient hydrogen production at a high power of 224 W with 43 % electricity consumption reduction.
Abstract
H2S is a prevalent yet toxic gas commonly encountered during fossil fuel extraction, whose electrolysis not only addresses pollution concerns but also facilitates hydrogen production. However, the advancement of H2S electrolysis at high current density has been impeded by the lack of stable and highly active electrodes that can endure the corrosive effects of H2S poisoning. Herein, we present an integrated-chainmail electrode that features dual-level chainmail structure with graphene encapsulating nickel foam (Ni@NC foam) to enhance H2S electrolysis. The electrode comprises a primary chainmail, formed by graphene coating on the surface of nickel foam, and a secondary chainmail, created by graphene encapsulating nickel nanoparticles. This integrated-chainmail structure significantly enhances both the activity and stability of nickel foam, which delivers an industrial-scale high current density exceeding 1 A cm−2 at 1.12 V versus reversible hydrogen electrode, above five times higher than nickel foam. Moreover, the Ni@NC foam remains stable over 300 hours of test, demonstrating a lifespan at least ten times longer than nickel foam. In a demo for H2S removal from simulated natural gas, the Ni@NC foam as the electrodes exhibits a hydrogen production rate of 272 ml min−1, while reducing electricity consumption by 43 % compared with traditional water electrolysis.