2025-12-02 清華大学
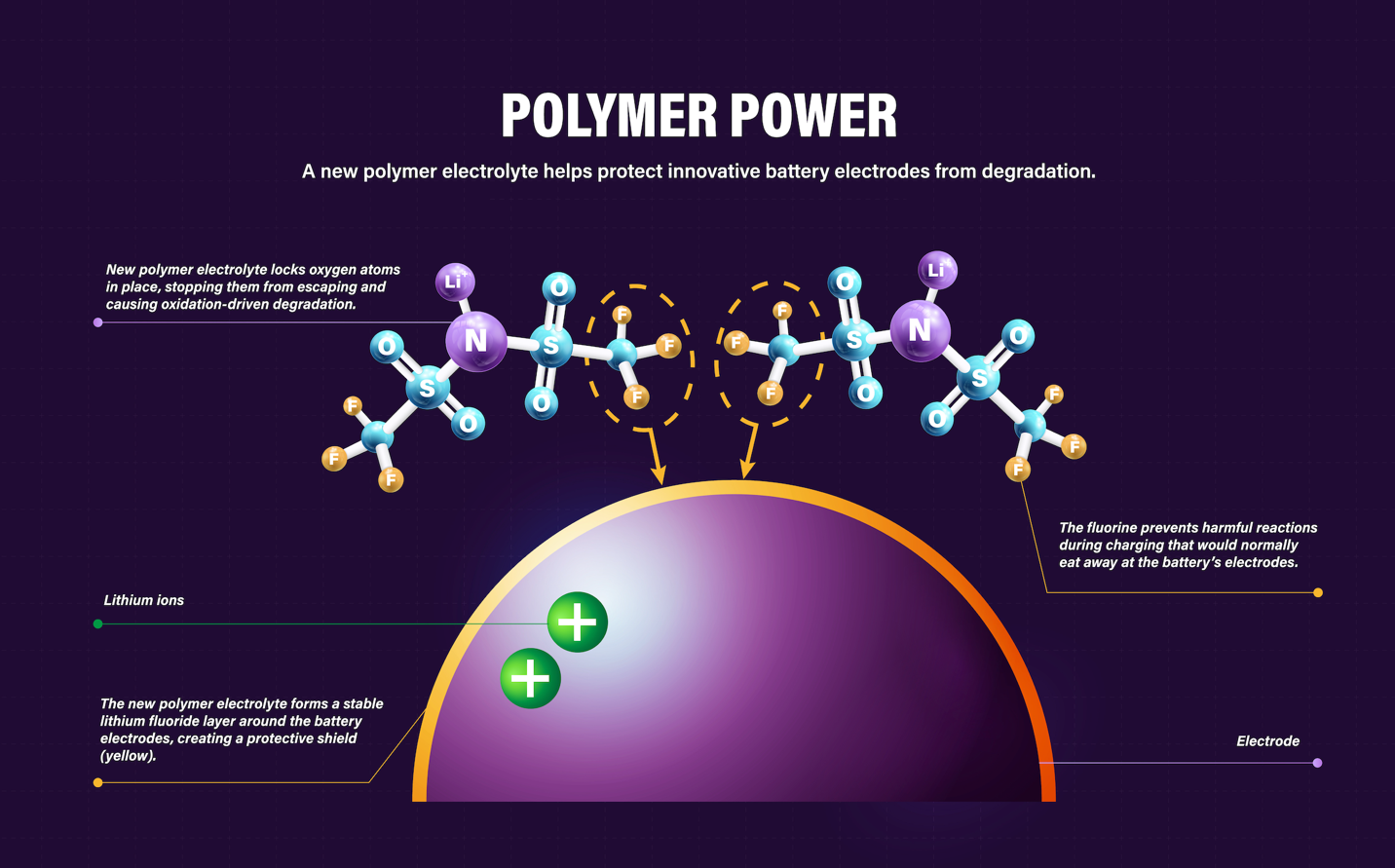
Fluorine-rich polymer electrolytes enable lighter, safer, high-voltage batteries, boosting energy density.
<関連情報>
- https://www.tsinghua.edu.cn/en/info/1245/14623.htm
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09565-z
600Wh/kgリチウム電池向けポリマー電解質溶媒和の調整 Tailoring polymer electrolyte solvation for 600 Wh kg−1 lithium batteries
Xue-Yan Huang,Chen-Zi Zhao,Wei-Jin Kong,Nan Yao,Zong-Yao Shuang,Pan Xu,Shuo Sun,Yang Lu,Wen-Ze Huang,Jin-Liang Li,Liang Shen,Xiang Chen,Jia-Qi Huang,Lynden A. Archer & Qiang Zhang
Nature Published:24 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09565-z
Abstract
Polymer electrolytes paired with lithium-rich manganese-based layered oxide (LRMO) cathodes and anode-free cell design are considered one of the most promising high-energy-density and high-safety systems1,2,3,4. However, the unstable anode morphological changes and the irreversible anionic reactions at the electrolyte–cathode interfaces induce oxygen escape and catalytic decomposition of polymer electrolytes, resulting in severe interfacial degradation and poor cycling stability. Here we design an in-built fluoropolyether-based polymer electrolyte composed of strongly solvating polyether and weakly solvating fluorohydrocarbon pendants, creating an anion-rich solvation structure and thus anion-derived fluorine-rich interfacial layers on the cathode and anode to resist interfacial issues. The LRMO cathode exhibits improved oxygen redox reversibility with substantially reduced oxygen-involving interfacial side reactions. This quasi-solid-state polymer electrolyte with 30 wt% trimethyl phosphate enables an LRMO cathode with a reversible high-areal-capacity cycling (>8 mAh cm−2) in pouch cells and long-term stability (>500 cycles at 25 °C) in coin cells, respectively. The pouch cells exhibit an energy density of 604 Wh kg−1 (1,027 Wh l−1) and excellent safety under a nail penetration at a fully charged condition. Our work, therefore, provides a promising direction for creating practical high-energy-density and high-safety lithium batteries.



