2025-11-25 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/earth/202511/t20251125_1133198.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43247-025-02882-1
過去10年間の北太平洋の温暖化の加速により、北極海の氷の減少が減速した Decelerated Arctic Sea ice loss triggered by accelerated North Pacific warming over the past decade
Lejiang Yu,Haibo Bi,Shiyuan Zhong,Peng Zhang & Cuijuan Sui
Communications Earth & Environment Published:18 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-025-02882-1
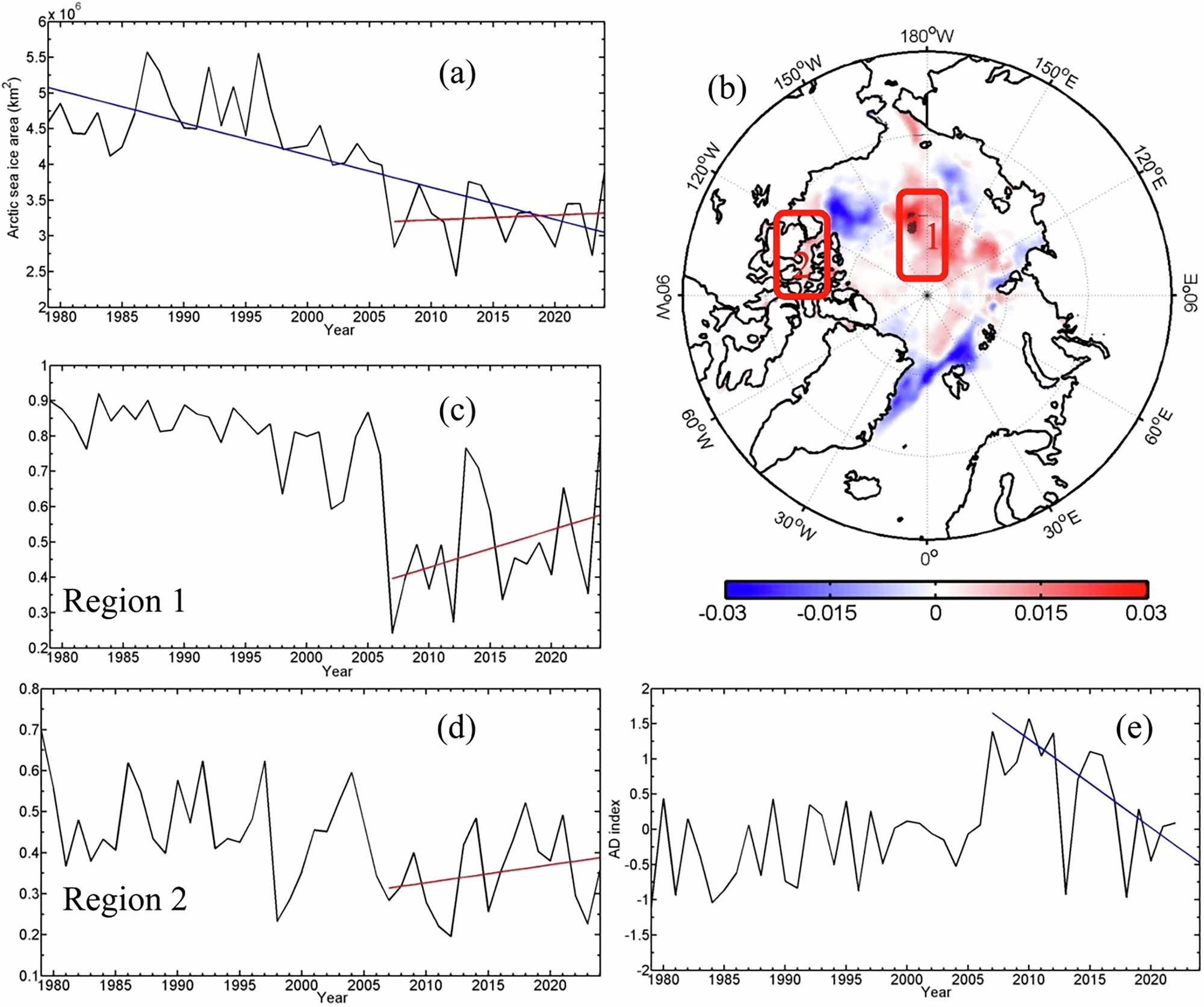
Abstract
As global mean surface temperatures have risen rapidly (approaching the 1.5 °C warming threshold), an unexpected slowdown in Arctic summer sea ice loss has been identified. Here, we use observational and numerical analysis and show that this divergence between Arctic and global warming trends stems from a positive sea surface temperature trend in the North Pacific. The warmed North Pacific Ocean triggers an atmospheric wavetrain that propagates into the Arctic, modifying large-scale wind and temperature patterns and consequently tempering the Arctic warming driven by global climate change. These circulation shifts enhance summer sea ice cover in localized regions, such as the Queen Elizabeth Islands and the central Arctic Ocean near 180 °, through wind-driven thermodynamic processes, partially offsetting sea ice losses elsewhere. The out-of-phase relationship between Arctic and North Pacific climate dynamics represents a critical mechanism regulating anthropogenically driven Arctic amplification, both in recent decades and likely into the near future.



