2025-06-16 オックスフォード大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2025-06-16-new-breakthrough-enables-precise-activation-quantum-features-diamond
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-60373-5
ダイヤモンドにおける単一IV族色中心のレーザー活性化 Laser activation of single group-IV colour centres in diamond
Xingrui Cheng,Andreas Thurn,Guangzhao Chen,Gareth S. Jones,James E. Bennett,Maddison Coke,Mason Adshead,Cathryn P. Michaels,Osman Balci,Andrea C. Ferrari,Mete Atatüre,Richard J. Curry,Jason M. Smith,Patrick S. Salter & Dorian A. Gangloff
Nature Communications Published:02 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60373-5
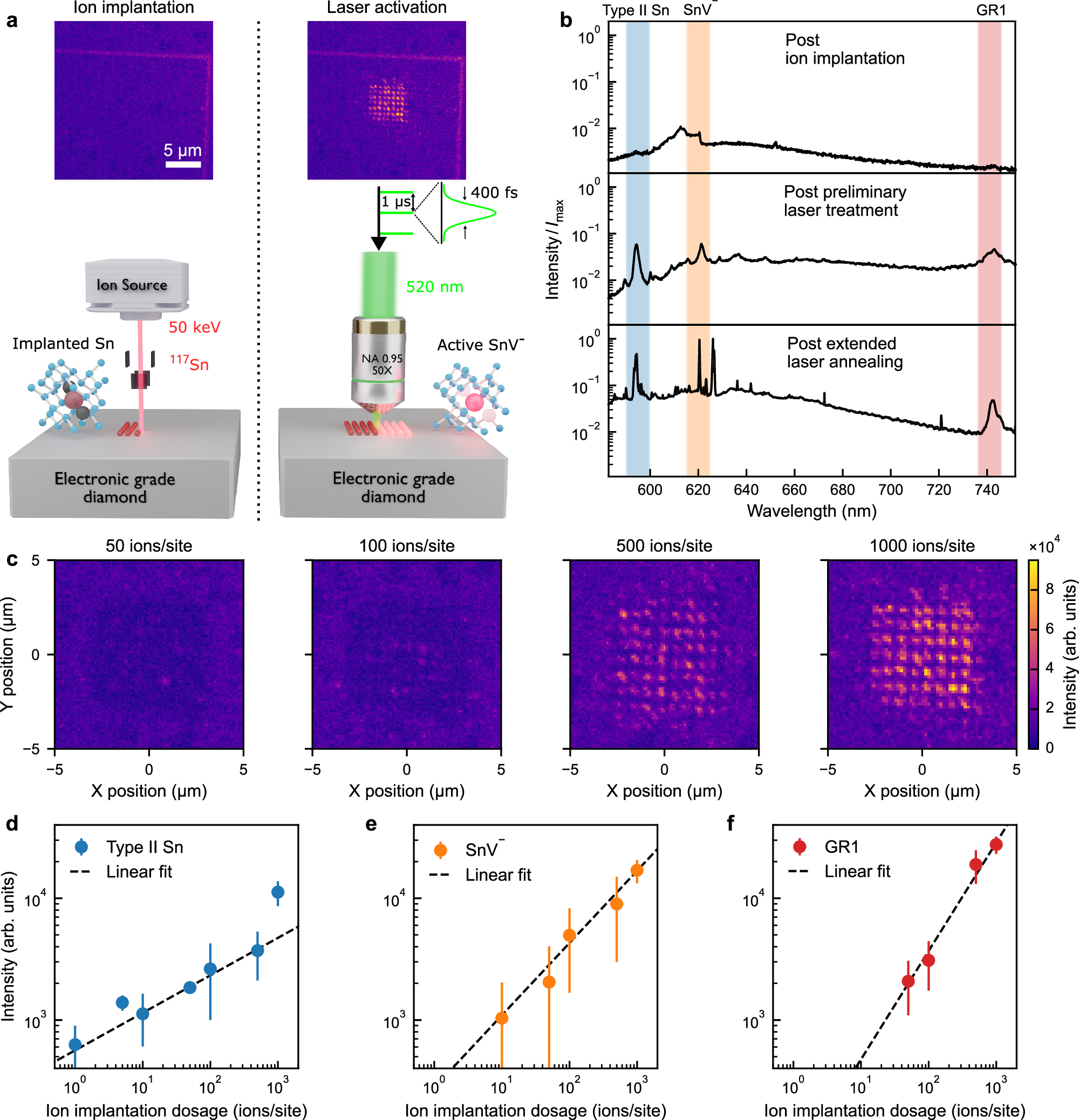
Abstract
Spin-photon interfaces based on group-IV colour centres in diamond offer a promising platform for quantum networks. A key challenge in the field is realising precise single-defect positioning and activation, which is crucial for scalable device fabrication. Here we address this problem by demonstrating a two-step fabrication method for tin vacancy (SnV−) centres that uses site-controlled ion implantation followed by local femtosecond laser annealing with in-situ spectral monitoring. The ion implantation is performed with sub-50 nm resolution and a dosage that is controlled from hundreds of ions down to single ions per site, limited by Poissonian statistics. Using this approach, we successfully demonstrate site-selective creation and modification of single SnV− centres. Our in-situ spectral monitoring opens a window onto materials tuning at the single defect level, and provides new insight into defect structures and dynamics during the annealing process. While demonstrated for SnV− centres, this versatile approach can be readily generalised to other implanted colour centres in diamond and wide-bandgap materials.



