2025-06-11 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
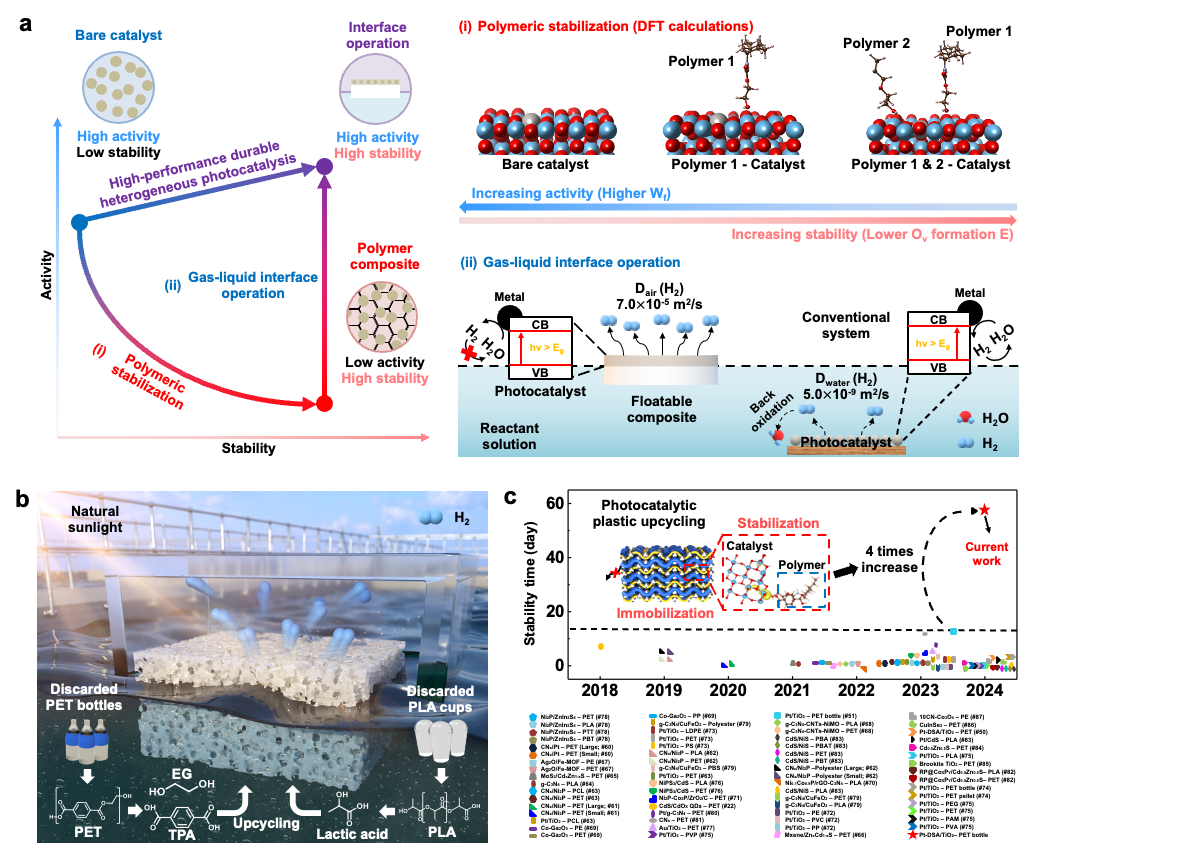
Figure 1. Turning Plastic Waste into Clean Hydrogen with Sunlight
<関連情報>
- https://ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=25929&pageIndex=1&searchCnd=&searchWrd=
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-025-01957-6
プラスチック廃棄物からの耐久性のあるソーラー水素製造のための気液界面での高分子安定化 Polymeric stabilization at the gas–liquid interface for durable solar hydrogen production from plastic waste
Wang Hee Lee,Hyunseo Park,Chan Woo Lee,Haeseong Kim,Jae Hwan Jeong,Jeong In Yun,Seong-Uk Bang,Junhyeok Heo,Kyung Hyun Ahn,Gi Doo Cha,Megalamane S. Bootharaju,Byoung-Hoon Lee,Jaeyune Ryu,Minho Kim,Taeghwan Hyeon & Dae-Hyeong Kim
Nature Nanotechnology Published:11 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-025-01957-6
Abstract
Heterogeneous photocatalysis offers substantial potential for sustainable energy conversion, yet its industrial application is constrained by limited durability under stringent photochemical conditions. Achieving high photocatalytic activity often requires harsh reaction conditions, compromising catalyst stability and longevity. Here we propose a strategy involving polymeric stabilization of photocatalytic centres uniquely localized at the gas–liquid interface, substantially enhancing both the catalytic activity and stability. Applied to the photocatalytic conversion of plastic waste into solar hydrogen, this approach maintained its catalytic performance over 2 months under harsh conditions. Using 0.3 wt% dynamically stabilized atomic Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts and concentrated sunlight, we achieved a plastic reforming activity of 271 mmolH2 h−1 m−2. Scaling to 1 m2 under natural sunlight yielded a hydrogen production rate of 0.906 l per day from polyethylene terephthalate waste. Economic analysis and extensive-scale simulations suggest this strategy as a promising pathway for high-performance, durable photocatalysis, advancing renewable energy conversion.