2025-05-14 中国科学院(CAS)
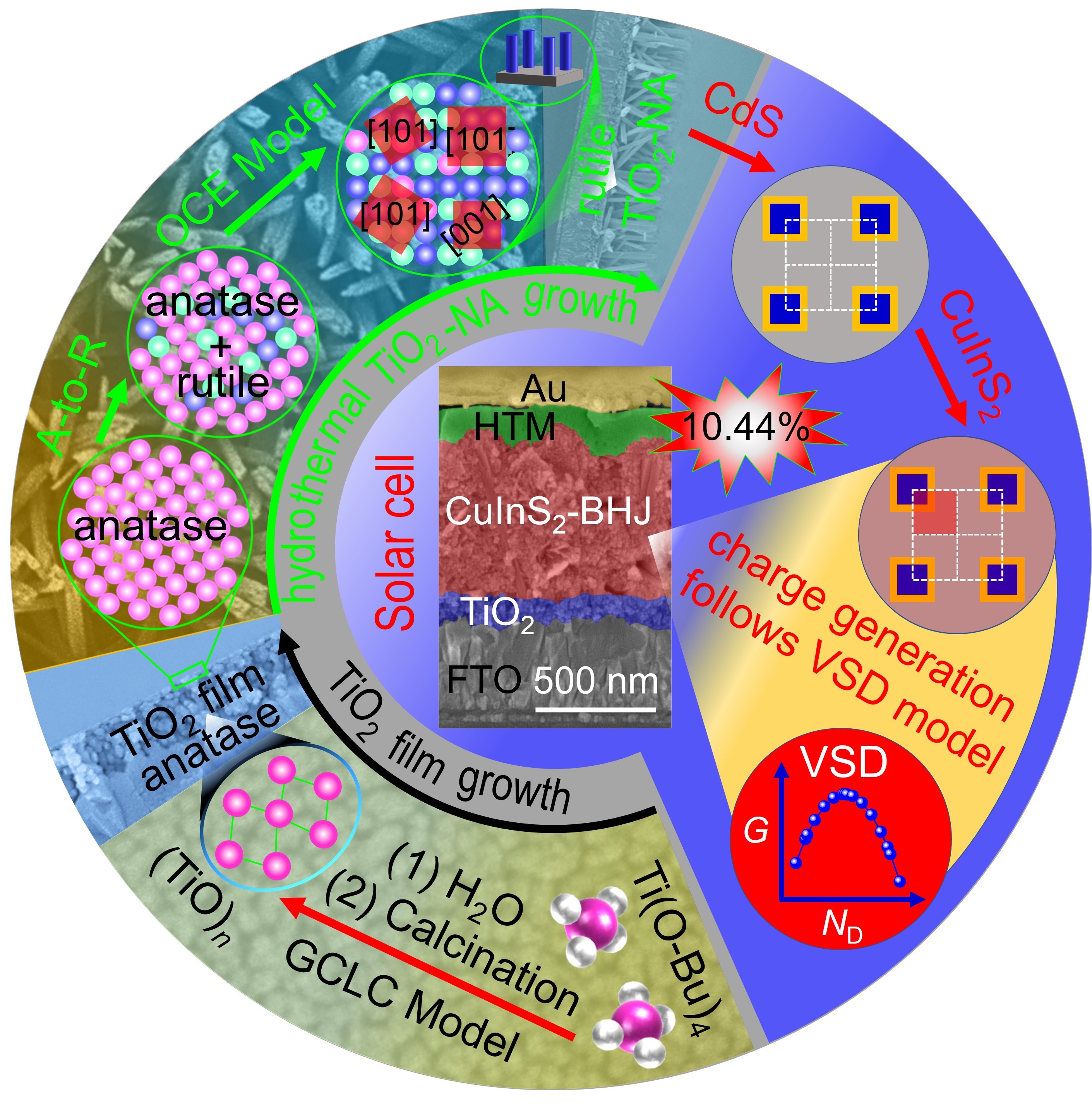 Schematic illustration of the TiO2-NA preparation technology, growth principles, solar cell structure, and carrier generation model. (Image by CAO Wenbo)
Schematic illustration of the TiO2-NA preparation technology, growth principles, solar cell structure, and carrier generation model. (Image by CAO Wenbo)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202505/t20250515_1043678.shtml
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smtd.202500264
効率的な太陽電池のための密度制御可能な酸化チタンナノロッドアレイにおける成長原理と光起電力原理を明らかにする Unveiling Growth and Photovoltaic Principles in Density-Controllable TiO2 Nanorod Arrays for Efficient Solar Cells
Wenbo Cao, Chao Dong, Chaofan Zheng, Jiajin Kuang, Yang Wang, Faisal Naveed, Mengqi Jin, Yingying Dong, Chong Chen, Mingtai Wang
Small Methods Published: 22 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202500264
Abstract
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanorod arrays (TiO2-NA) are widely used in optoelectronic devices. Controlling the number density (ND) of nanorods without altering their dimensional features in TiO2-NA is of great importance to the tailored performance of the optoelectronic devices, which unfortunately remains challenging up to now. Here, a facile strategy is developed to control the ND without changing the TiO2 nanorod sizes in the rutile TiO2-NAs hydrothermally grown on an anatase TiO2 film on a large scale. Moreover, ND-controllable TiO2-NAs are applied to CuInS2 solar cells, achieving a champion efficiency of 10.44% for solution-processed CuInS2 solar cells. It is found that the hydrolysis time (tH) in preparing the anatase TiO2 film provides good control over ND in TiO2-NA as the result of tH-governed nanoparticle size in the anatase TiO2 film. A gel-chain-limited crystallization model for tH-governed anatase TiO2 nanoparticle size, an orientation-competing-epitaxial nucleation/growth model for the out-of-plane growth of single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanorod on polycrystalline anatase TiO2 film, and a volume-surface-density model for the ND-governed photocurrent generation in nanoarray-based solar cells are proposed.