2025-02-12 フィンランド・リンショーピング大学 (LiU)
<関連情報>
- https://liu.se/en/news-item/nasta-generations-solcell-ar-helt-atervinningsbar
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-08408-7
ペロブスカイト太陽電池の水系リサイクル Aqueous-based recycling of perovskite photovoltaics
Xun Xiao,Niansheng Xu,Xueyu Tian,Tiankai Zhang,Bingzheng Wang,Xiaoming Wang,Yeming Xian,Chunyuan Lu,Xiangyu Ou,Yanfa Yan,Licheng Sun,Fengqi You & Feng Gao
Nature Published:12 February 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-08408-7
Abstract
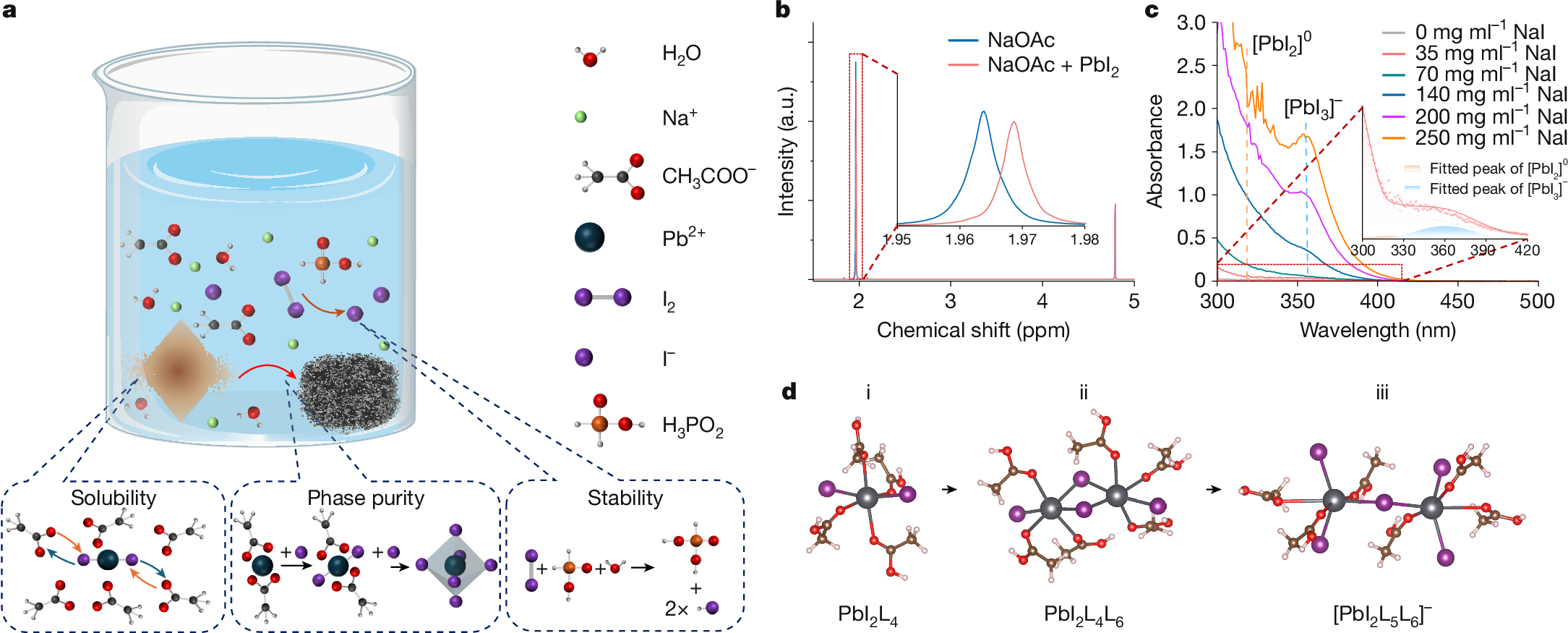
Cumulative silicon photovoltaic (PV) waste highlights the importance of considering waste recycling before the commercialization of emerging PV technologies1,2. Perovskite PVs are a promising next-generation technology3, in which recycling their end-of-life waste can reduce the toxic waste and retain resources4,5. Here we report a low-cost, green-solvent-based holistic recycling strategy to restore all valuable components from perovskite PV waste. We develop an efficient aqueous-based perovskite recycling approach that can also rejuvenate degraded perovskites. We further extend the scope of recycling to charge-transport layers, substrates, cover glasses and metal electrodes. After repeated degradation–recycling processes, the recycled devices show similar efficiency and stability compared with the fresh devices. Our holistic recycling strategy reduces by 96.6% resource depletion and by 68.8% human toxicity (cancer effects) impacts associated with perovskite PVs compared with the landfill treatment. With recycling, the levelized cost of electricity also decreases for both utility-scale and residential systems. This study highlights unique opportunities of perovskite PVs for holistic recycling and paves the way for a sustainable perovskite solar economy.



