2025-01-30 ペンシルベニア州立大学 (PennState)
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/earth-and-mineral-sciences/story/new-method-sustainable-lithium-extraction-could-reduce-emissions
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-48867-0
電気化学的浸出法による鉱石からのリチウムの直接抽出 Direct extraction of lithium from ores by electrochemical leaching
Hanrui Zhang,Ying Han,Jianwei Lai,Joseph Wolf,Zhen Lei,Yang Yang & Feifei Shi
Nature communications Published:13 June 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48867-0
Abstract
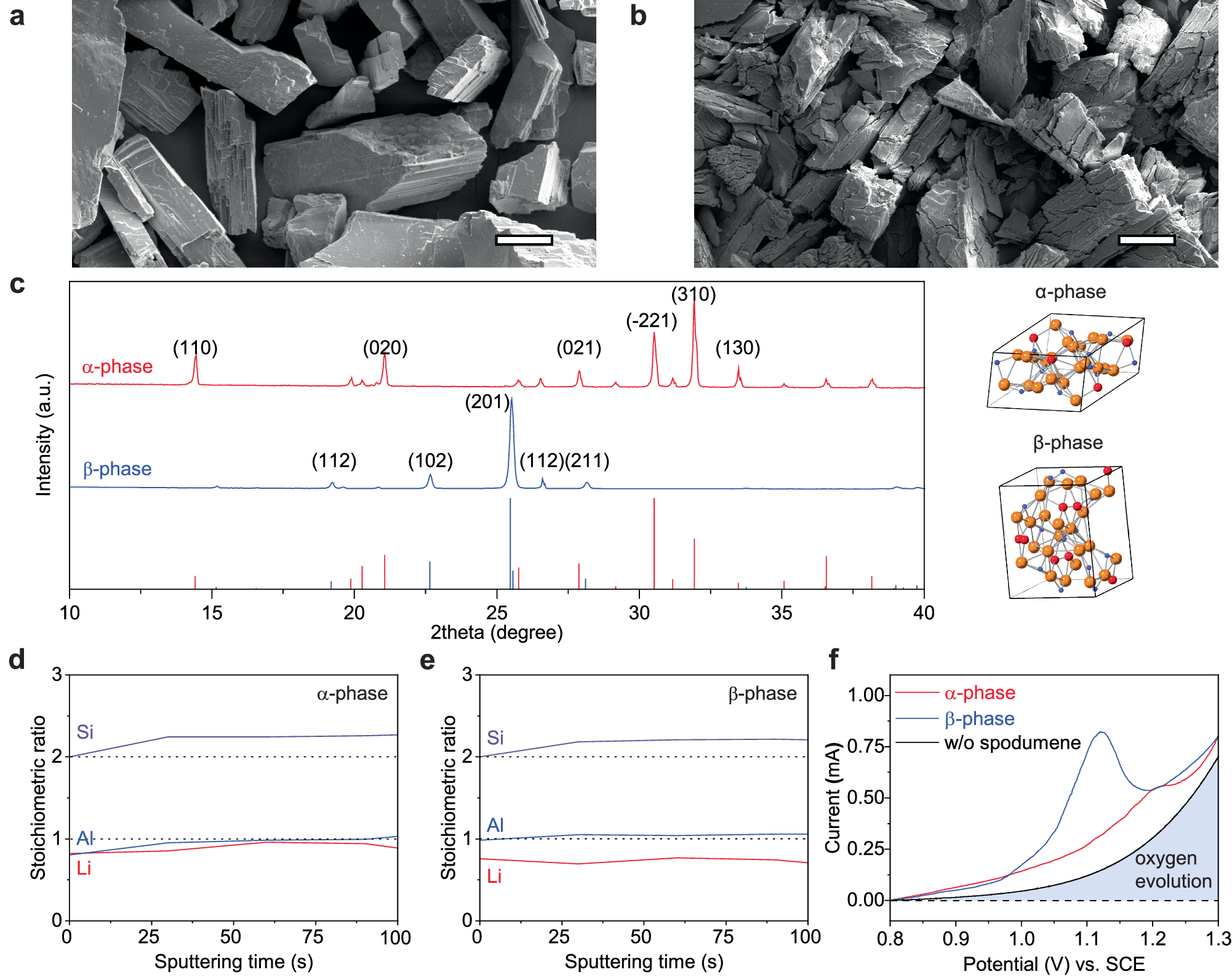
With the rapid increase in lithium consumption for electric vehicle applications, its price soared during the past decade. To secure a reliable and cost-effective supply chain, it is critical to unlock alternative lithium extraction resources beyond conventional brine. In this study, we develop an electrochemical method to directly leach lithium from α-phase spodumene. We find the H2O2 promoter can significantly reduce the leaching potential by facilitating the electron transfer and changing the reaction path. Upon leaching, β-phase spodumene shows a typical phase transformation to HAlSi2O6, while leached α-phase remains its original crystal phase with a lattice shrinkage. To demonstrate the scale-up potential of electrochemical leaching, we design a catalyst-modified high-throughput current collector for high loading of suspended spodumene, achieving a leaching current of 18 mA and a leaching efficiency of 92.2%. Electrochemical leaching will revolutionize traditional leaching and recycling processes by minimizing the environmental footprint and energy consumption.



