2025-01-20 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/infrared-heat-transfers
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-024-01723-6
振動の弱結合と強結合が空洞を介した放射エネルギー移動によって化学反応を修飾する Vibrational weak and strong coupling modify a chemical reaction via cavity-mediated radiative energy transfer
Zachary T. Brawley,Sindhana Pannir-Sivajothi,Ju Eun Yim,Yong Rui Poh,Joel Yuen-Zhou & Matthew Sheldon
Nature Chemistry Published:16 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-024-01723-6
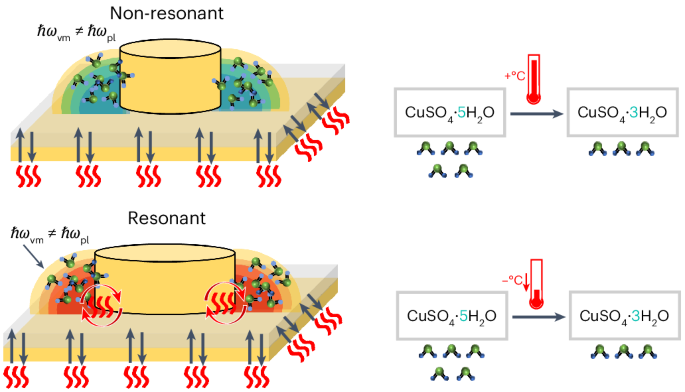
Abstract
Controlling reaction outcomes through external influences is a central goal in chemistry. Vibrational coupling between molecular vibrations and cavity modes is rapidly emerging as a distinct strategy compared with conventional thermochemical and photochemical methods; however, insight into the fundamental mechanisms remains limited. Here we investigate how vibrational weak and strong coupling in plasmonic nanocavities modifies the thermal dehydration of copper sulfate pentahydrate. We demonstrate that light–matter coupling reduces the onset temperature for dehydration by up to 14 °C, and we attribute this effect to enhanced radiative energy transport that is mediated by resonant electromagnetic modes, eliminating temperature gradients in the coupled system. Our findings provide direct evidence of localized energy transfer leading to modified chemical behaviour in specific regions of high optical density of states. This work establishes a mechanism for modifying thermally driven chemical processes using optical cavities, with implications for the development of catalytic systems that exploit these tailored interactions to achieve targeted reaction control.