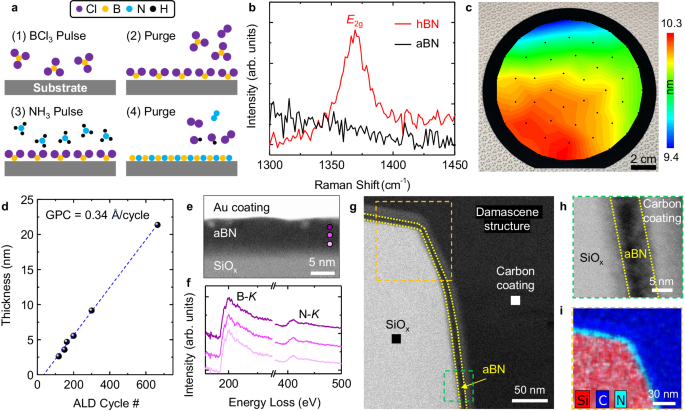
2024-09-15 コロンビア大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.engineering.columbia.edu/about/news/new-battery-technology-could-boost-renewable-energy-storage
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-51905-6
高エネルギー密度で低コストのK-Na/S電池のための硫化物/二硫化物の溶解度の高い電解質の設計 Designing electrolytes with high solubility of sulfides/disulfides for high-energy-density and low-cost K-Na/S batteries
Liying Tian,Zhenghao Yang,Shiyi Yuan,Tye Milazzo,Qian Cheng,Syed Rasool,Wenrui Lei,Wenbo Li,Yucheng Yang,Tianwei Jin,Shengyu Cong,Joseph Francis Wild,Yonghua Du,Tengfei Luo,Donghui Long & Yuan Yang
Nature Communications Published:05 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-51905-6
Abstract
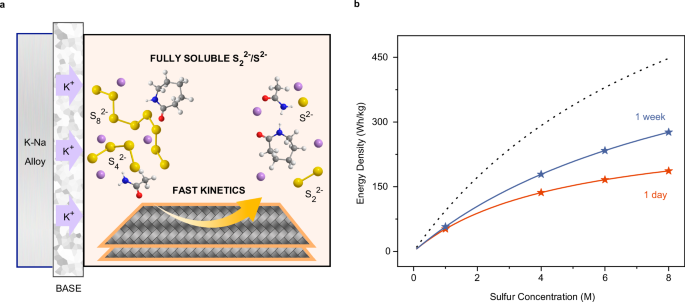
Alkaline metal sulfur (AMS) batteries offer a promising solution for grid-level energy storage due to their low cost and long cycle life. However, the formation of solid compounds such as M2S2 and M2S (M = Na, K) during cycling limits their performance. Here we unveil intermediate-temperature K-Na/S batteries utilizing advanced electrolytes that dissolve all polysulfides and sulfides (K2Sx, x = 1–8), significantly enhancing reaction kinetics, specific capacity, and energy density. These batteries achieve near-theoretical capacity (1655 mAh g−1 sulfur) at 75 °C with a 1 M sulfur concentration. At a 4 M sulfur concentration, they deliver 830 mAh g−1 at 2 mA cm−2, retaining 71% capacity after 1000 cycles. This new K-Na/S battery with specific energy of 150-250 Wh kg−1 only employs earth-abundant elements, making it attractive for long-duration energy storage.