2024-08-19 パデュー大学

Photo provided by Getty Images
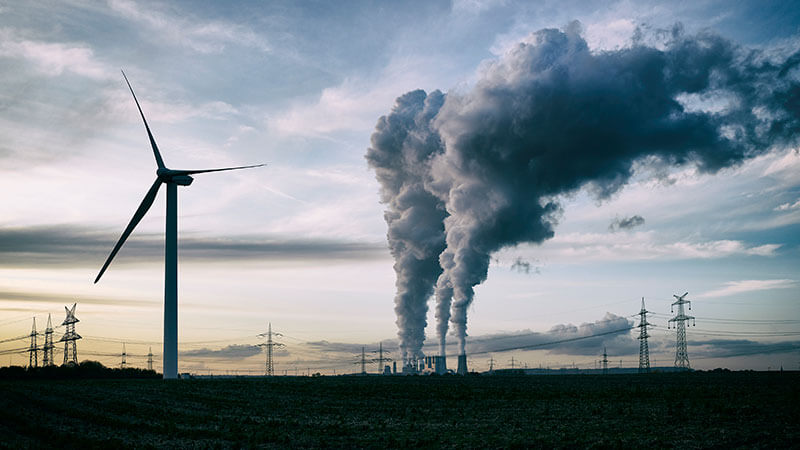
◆パデュー大学の研究によると、風力タービンはクリーンエネルギー供給だけでなく、既存のCO2捕集技術よりも低コストでCO2を除去できることが判明しました。
◆風力タービンの後流でタービンブレードの先端の上下両方で CO 2の初期濃度がタービン上で高かった場合、CO 2の巻き込みが発生しました。この研究は、風力タービンが回転する際に生じる空気の渦がCO2を効率的に捕集できることを示しています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.purdue.edu/research/features/stories/purdue-research-more-than-green-energy-wind-turbines-are-cost-saving-co2-eliminators/
- https://pubs.aip.org/aip/jrse/article-abstract/16/2/023304/3272535/Potential-of-wind-turbines-on-the-alteration-of

二酸化炭素濃度の変化に対する風力タービンの可能性
Potential of wind turbines on the alteration of carbon dioxide concentration
Venkatesh Pulletikurthi;Clarice Nelson;Luciano Castillo
Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Published:March 14 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0179608
Anthropogenic carbondioxide (CO2) emissions are a major factor in global warming, requiring significant cuts to combat climate change. A crucial technology to reduce global CO2 concentration is direct air capture (DAC) of CO2. However, existing DAC techniques are expensive because of low CO2 concentrations, and they frequently rely on fossil fuel-based energy. In this article, we investigate how wind turbines can influence local CO2 levels and potentially collaborate with DAC and other technologies. To explore this idea, we performed large-eddy simulations using two 5 MW commercial-scale wind turbines. We incorporated realistic CO2 profiles collected from 13 different global locations across different seasons. The simulations were performed under neutral atmospheric boundary layer conditions. The results demonstrate that the wake recovery mechanism of a wind turbine promotes rapid mixing of CO2 both above and below the turbine blade tips in the wind turbine wake. In cases where the initial concentrations of CO2 were elevated above the turbine, downward entrainment of CO2 occurred. Conversely, when high concentrations of CO2 were present in the lower atmosphere, wind turbines facilitated a decrease in concentration at that layer by up to 138 kg/m within the intermediate wake (within 7 diameters) of the second turbine, T2. These discoveries inspire further investigation into the potential synergies between wind turbines and DAC devices or local CO2 pollutant diverters, depending on the prevailing CO2 profile. Consequently, this article marks the initial showcase of wind turbines’ capability to influence CO2 levels by creating an entrainment and removal effect.