2026-02-16 大阪大学 産業科学研究所
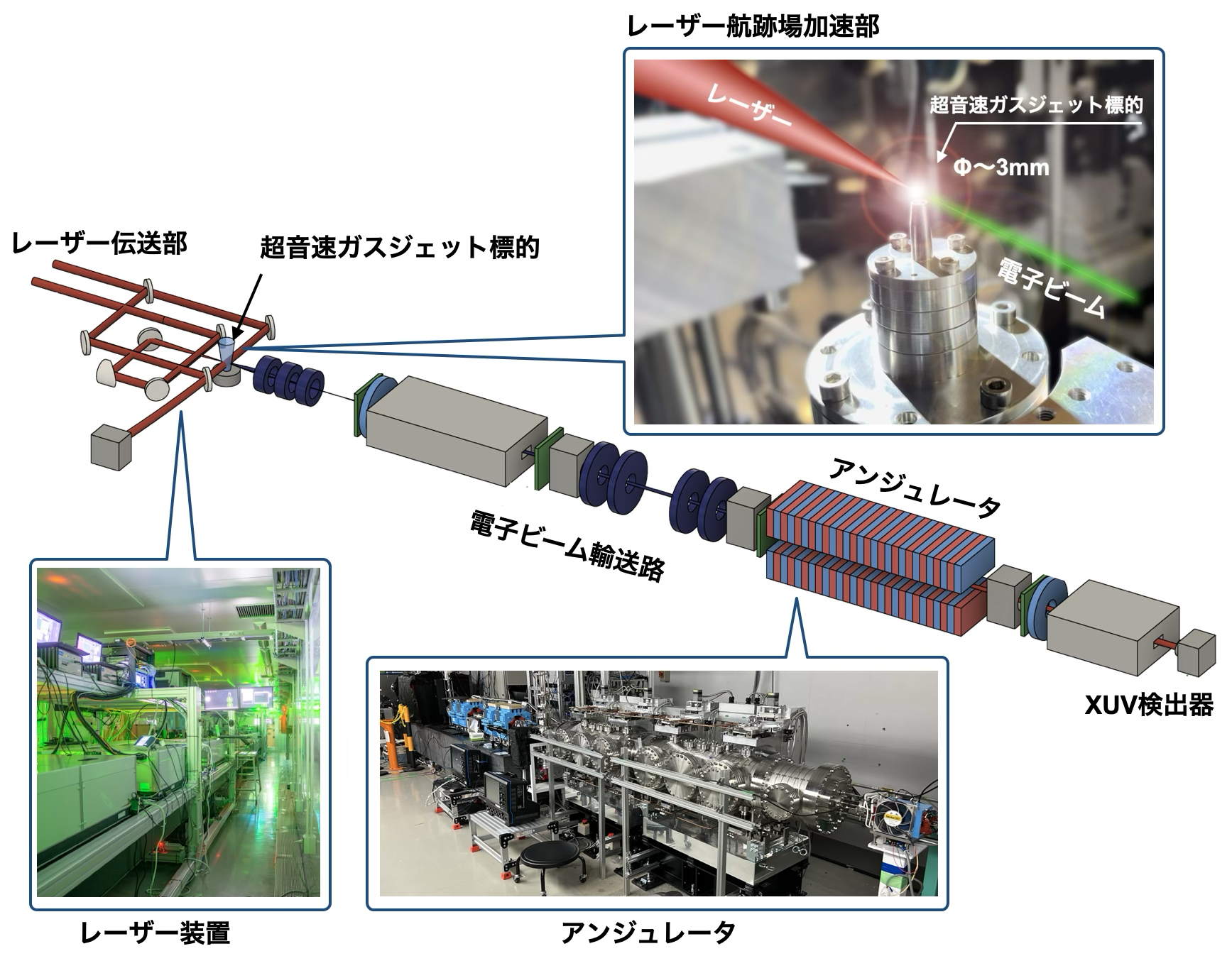
図1 LWFAの電子ビームを用いたXUVのFEL実証実験の概略図
<関連情報>
- https://www.sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp/achievement/release/20260216.html
- https://journals.aps.org/prresearch/accepted/10.1103/qvg7-ng8n
最適化されたレーザー航跡場加速:安定した高エネルギーの単一エネルギー電子ビームを生成し、極端紫外線自由電子レーザーを実証する Optimized laser wakefield acceleration: Generating stable, high-energy, monoenergetic electron beams and demonstrating extreme-ultraviolet free-electron lasers
Zhan Jin and Masaki Kando and Yan-Jun Gu and Kai Huang and Nobuhiko Nakanii and Izuru Daito and Zhenzhe Lei and Shingo Sato and Hiroaki Sano and Toshiya Muto and Shigeru Yamamoto and Tomonao Hosokai
Physical Review Research Accepted: 6 January, 2026
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/qvg7-ng8n
Abstract
Free-electron lasers (FELs) are powerful, tunable light sources capable of delivering ultrashort, coherent radiation over a wide spectral range, but their broad scientific and technological impact is limited by the size and cost of large-scale accelerators. Laser wakefield acceleration (LWFA) offers a compact alternative via the ultra-high accelerating gradients, though achieving FEL gain with such beams remains a major challenge due to the stringent beam quality requirements. Here we present a successful demonstration of a laser-plasma accelerator-driven FEL operating at a central wavelength of 40 nm with a highly nonlinear gain. A compact 0.8 J laser system, combined with precise control over the plasma density profile, injection conditions, and the stability of both laser wavefront and gas jet, enabled the generation of high-quality monoenergetic electron beams with excellent shot-to-shot reproducibility. A comprehensive start-to-end simulation framework was established, incorporating beam acceleration, transport, and FEL generation. Each stage of the simulation shows good agreement with the experimental diagnostics. The resulting FEL radiation exhibits clear exponential gain of approximately 20 times. This work highlights a reliable route toward compact, tunable, X-ray FELs driven by LWFA, and represents a significant step toward practical applications of laser-plasma-based light sources.