2026-01-07 ニューヨーク大学(NYU)
<関連情報>
- https://www.nyu.edu/about/news-publications/news/2026/january/human-ancestors-in-morocco-reveal-an-african-lineage-near-the-ro.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09914-y
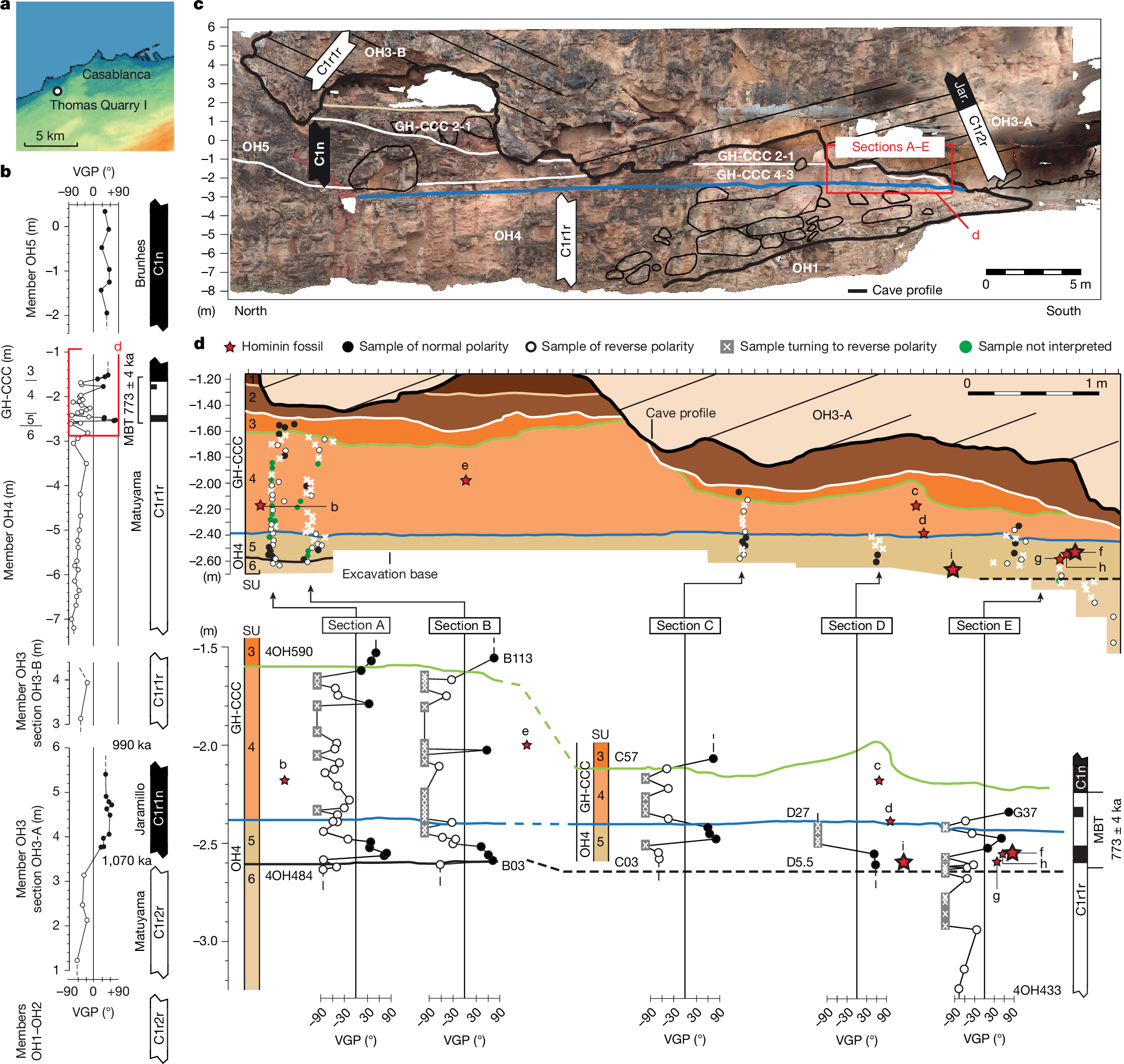
モロッコのホモ・サピエンス系統の基底人類 Early hominins from Morocco basal to the Homo sapiens lineage
Jean-Jacques Hublin,David Lefèvre,Serena Perini,Giovanni Muttoni,Matthew M. Skinner,Shara E. Bailey,Sarah Freidline,Philipp Gunz,Mathieu Rué,Mohssine El Graoui,Denis Geraads,Camille Daujeard,Thomas W. Davies,Kornelius Kupczik,Mykolas D. Imbrasas,Alejandra Ortiz,Christophe Falguères,Qingfeng Shao,Jean-Jacques Bahain,Alain Queffelec,Asier Gómez-Olivencia,Stefano Benazzi,Adeline Le Cabec,Rita Sorrentino,… Abderrahim Mohib
Nature Published:07 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09914-y
Abstract
Palaeogenetic evidence suggests that the last common ancestor of present-day humans, Neanderthals and Denisovans lived around 765–550 thousand years ago (ka)1. However, both the geographical distribution and the morphology of these ancestral humans remain uncertain. The Homo antecessor fossils from the TD6 layer of Gran Dolina at Atapuerca, Spain, dated between 950 ka and 770 ka (ref. 2), have been proposed as potential candidates for this ancestral population3. However, all securely dated Homo sapiens fossils before 90 ka were found either in Africa or at the gateway to Asia, strongly suggesting an African rather than a Eurasian origin of our species. Here we describe new hominin fossils from the Grotte à Hominidés at Thomas Quarry I (ThI-GH) in Casablanca, Morocco, dated to around 773 ka. These fossils are similar in age to H. antecessor, yet are morphologically distinct, displaying a combination of primitive traits and of derived features reminiscent of later H. sapiens and Eurasian archaic hominins. The ThI-GH hominins provide insights into African populations predating the earliest H. sapiens individuals discovered at Jebel Irhoud in Morocco4 and provide strong evidence for an African lineage ancestral to our species. These fossils offer clues about the last common ancestor shared with Neanderthals and Denisovans.



