2025-12-18 国際農研,農研機構
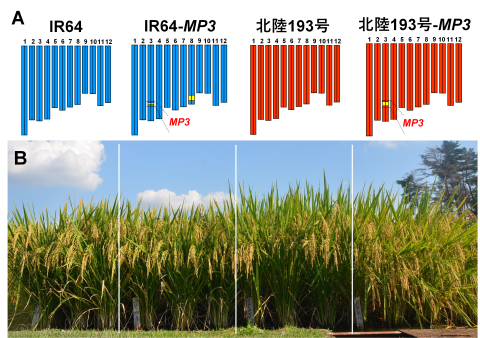
図1 MP3が導入された新系統と親品種の成熟期の草姿比較
イネの12本ある染色体の中で、3番目に位置するMP3が「コシヒカリ」由来となった新系統「IR64-MP3」と「北陸193号-MP3」を開発しました (A)。「北陸193号-MP3 」は親品種「北陸193号」よりも穂がたわわに実っていることが分かります (B) (令和6年9月撮影、場所は、国際農研八幡台圃場)。
<関連情報>
- https://www.jircas.go.jp/ja/release/2025/press202522
- https://www.jircas.go.jp/system/files/press/press202522.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378429024003198?via%3Dihub
穂数増加のための量的形質遺伝子座MP3は、高供給源および転座形質と結合することで、日本のイネの収量潜在力を向上させる MP3, a quantitative trait locus for increased panicle number, improves rice yield potential in Japan by connecting with high source and translocation traits
Toshiyuki Takai, Aung Zaw Oo, Takanori Okamoto, Hiroshi Nakano
Field Crops Research Available online: 7 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2024.109566
Highlights
- MP3 increased panicle number and sink size irrespective of N-applied treatments.
- MP3 increased grain yield in a cultivar with high source and translocation traits.
- The yield increase was attributed to sustained starch synthase gene expression.
- The yield increase was achieved without increasing N uptake.
Abstract
Context: I
ncreasing rice yield potential is an important strategy for meeting rising food demand and achieving global food security. MP3 was recently identified as a quantitative trait locus (QTL) in rice that increases panicle number and thereby sink size (the total number of spikelets per square meter). Under current climatic conditions, MP3 did not increase grain yield in a high-yielding cultivar in the absence of improved source traits.
Objective:
This study aimed to determine whether MP3 increases grain yield in a rice cultivar background with improved biomass production and to analyze the key variables linked to yield improvement.
Methods
Two-year experiments were carried out on a paddy field with nitrogen (N) applications in Tsukuba, Japan. Near-isogenic MP3 lines, Hokuriku 193-MP3 and IR64-MP3, were used in conjunction with their parental cultivars. Hokuriku 193 is a high-yielding cultivar in Japan with high biomass production, and IR64 is a high-yielding mega-cultivar in the tropics.
Results
Both Hokuriku 193-MP3 and IR64-MP3 increased panicle quantity and sink size when compared to the parental cultivars, regardless of N treatment. Hokuriku 193-MP3 had a 7 % higher grain yield than Hokuriku 193; however, IR64-MP3 did not yield more than IR64. Hokuriku 193 and Hokuriku 193-MP3 had larger leaf areas, higher biomass, and accumulated more non-structural carbohydrate (NSC) in the culms and leaf sheaths at heading than IR64 and IR64-MP3. Hokuriku 193-MP3 significantly reduced the NSC level in the culm and leaf sheaths at 16 d after heading and had a higher harvest index than Hokuriku 193; however, IR64-MP3 did not differ from IR64 with regard to these variables.
Conclusion
Hokuriku 193 has surplus source and translocation abilities that can fill the MP3-enlarged sink, resulting in a higher grain yield. In comparison, IR64 lacks these abilities. These findings imply that MP3 has boosted the yield potential of rice cultivars in Japan, with Hokuriku 193 having the highest yield in Japan.
Significance
This study shows that balanced improvements in sink, source, and translocation are essential for increasing rice yield potential. MP3 and the high source and translocation traits of Hokuriku 193 could benefit future high yield breeding initiatives around the world.



 個人 エアー・ボーンエッジX-R582(超軽量動力機、複座)の事故[墜落](茨城県坂東市 坂東フライングクラブ場外離着陸場付近、令和7年3月2日発生)](https://tiisys.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/スクリーンショット-2025-12-18-170042-500x279.png)