2025-10-13 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202510/t20251014_1089413.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-64022-9
表面上の原子スピンの電気的に調整可能な量子干渉 Electrically tunable quantum interference of atomic spins on surfaces
Hao Wang,Jing Chen,Peng Fan,Yelko del Castillo,Alejandro Ferrón,Lili Jiang,Zilong Wu,Shijie Li,Hong-Jun Gao,Heng Fan,Joaquín Fernández-Rossier & Kai Yang
Nature Communications Published:09 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64022-9
Abstract
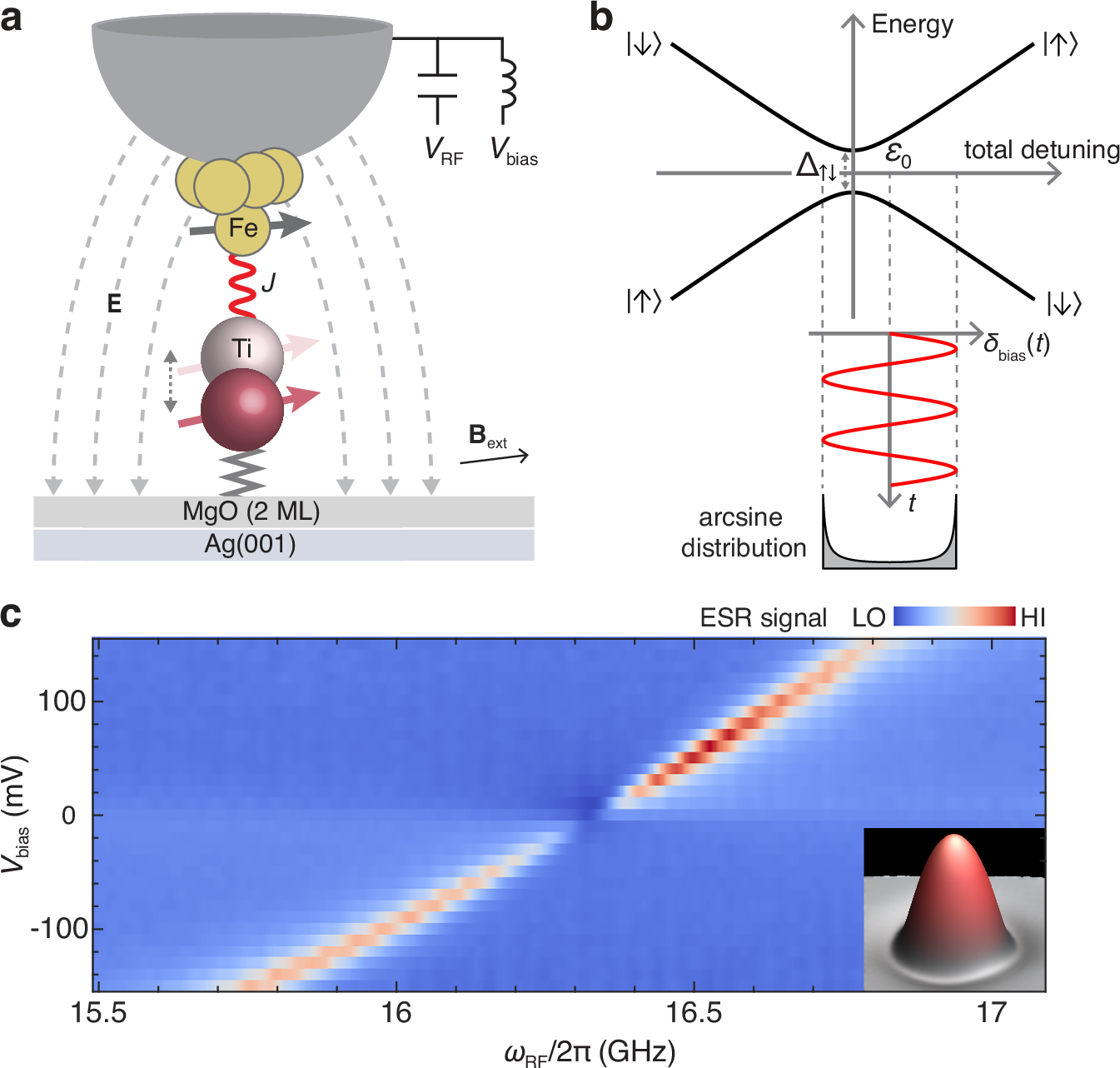
Controlling quantum interference near avoided energy-level crossings is crucial for fast and reliable coherent manipulation in quantum information processing. However, achieving tunable quantum interference in atomically-precise engineered structures remains challenging. Here, we demonstrate electrical control of quantum interference using atomic spins on an insulating film in a scanning tunneling microscope. Using bias voltages applied across the tunnel junction, we modulate the atomically-confined magnetic interaction between the probe tip and surface atoms with a strong electric field, and drive the spin state rapidly through the energy-level anticrossing. This all-electrical manipulation allows us to achieve Landau-Zener-Stückelberg-Majorana (LZSM) interferometry on both single spins and pairs of interacting spins. The LZSM pattern exhibits multiphoton resonances, and its asymmetry suggests that the spin dynamics is influenced by spin-transfer torque of tunneling electrons. Multi-level LZSM spectra measured on coupled spins with tunable interactions show distinct interference patterns depending on their many-body energy landscapes. These results open new avenues for all-electrical quantum manipulation in spin-based quantum processors in the strongly driven regime.