2025-02-24 シンガポール国立大学(NUS)
<関連情報>
- https://news.nus.edu.sg/new-designer-2d-materials-with-a-twist/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01748-5
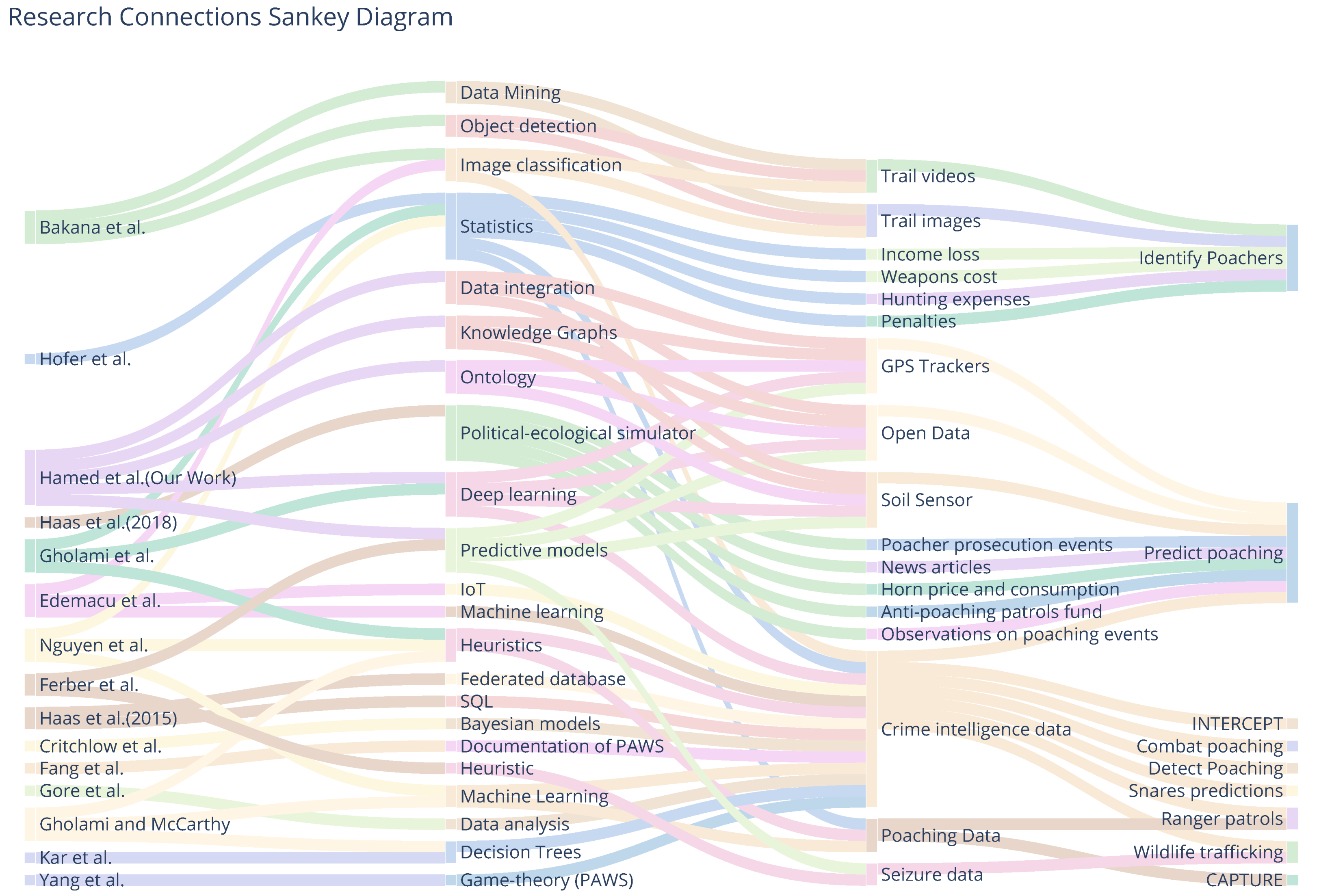
モアレ二次元共有結合有機フレームワーク超格子 Moiré two-dimensional covalent organic framework superlattices
Gaolei Zhan,Brecht Koek,Yijia Yuan,Yikuan Liu,Vipin Mishra,Veniero Lenzi,Karol Strutyński,Chunxiao Li,Rongrong Zhang,Xin Zhou,Hwa Seob Choi,Zhen-Feng Cai,Joaquín Almarza,Kunal S. Mali,Aurelio Mateo-Alonso,Manuel Melle Franco,Yihan Zhu,Steven De Feyter & Kian Ping Loh
Nature Chemistry Published:20 February 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-025-01748-5
Abstract
The on-surface synthesis of two-dimensional (2D) polymers from monomers represents a useful strategy for designing lattice, orbital and spin symmetries. Like other 2D materials, the ordered stacking of 2D polymers into bilayers may allow developing unique optoelectronic, charge transport and magnetic properties not found in the individual layers. However, controlling layer stacking of 2D polymers remains challenging. Here we describe a method for synthesizing 2D polymer bilayers or bilayer 2D covalent organic frameworks at the liquid–substrate interface through the direct condensation of monomers. More importantly, we also show how factors such as monomer structure and solvent mixture influence the bilayer stacking modes and how, under certain conditions, large-area moiré superlattices emerge from the twisted bilayer stacking. This finding offers new opportunities for the design of bilayer stacked framework materials with tunable electronic and structural properties.