2024-10-18 アメリカ合衆国・シカゴ大学
<関連情報>
- https://pme.uchicago.edu/news/new-diamond-bonding-technique-breakthrough-quantum-devices
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-53150-3
ヘテロジニアス量子・電子技術のための直接結合ダイヤモンド膜 Direct-bonded diamond membranes for heterogeneous quantum and electronic technologies
Xinghan Guo, Mouzhe Xie, Anchita Addhya, Avery Linder, Uri Zvi, Stella Wang, Xiaofei Yu, Tanvi D. Deshmukh, Yuzi Liu, Ian N. Hammock, Zixi Li, Clayton T. DeVault, Amy Butcher, Aaron P. Esser-Kahn, David D. Awschalom, Nazar Delegan, Peter C. Maurer, F. Joseph Heremans & Alexander A. High
Nature Communications PublishedDOIhttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53150-3
Abstract
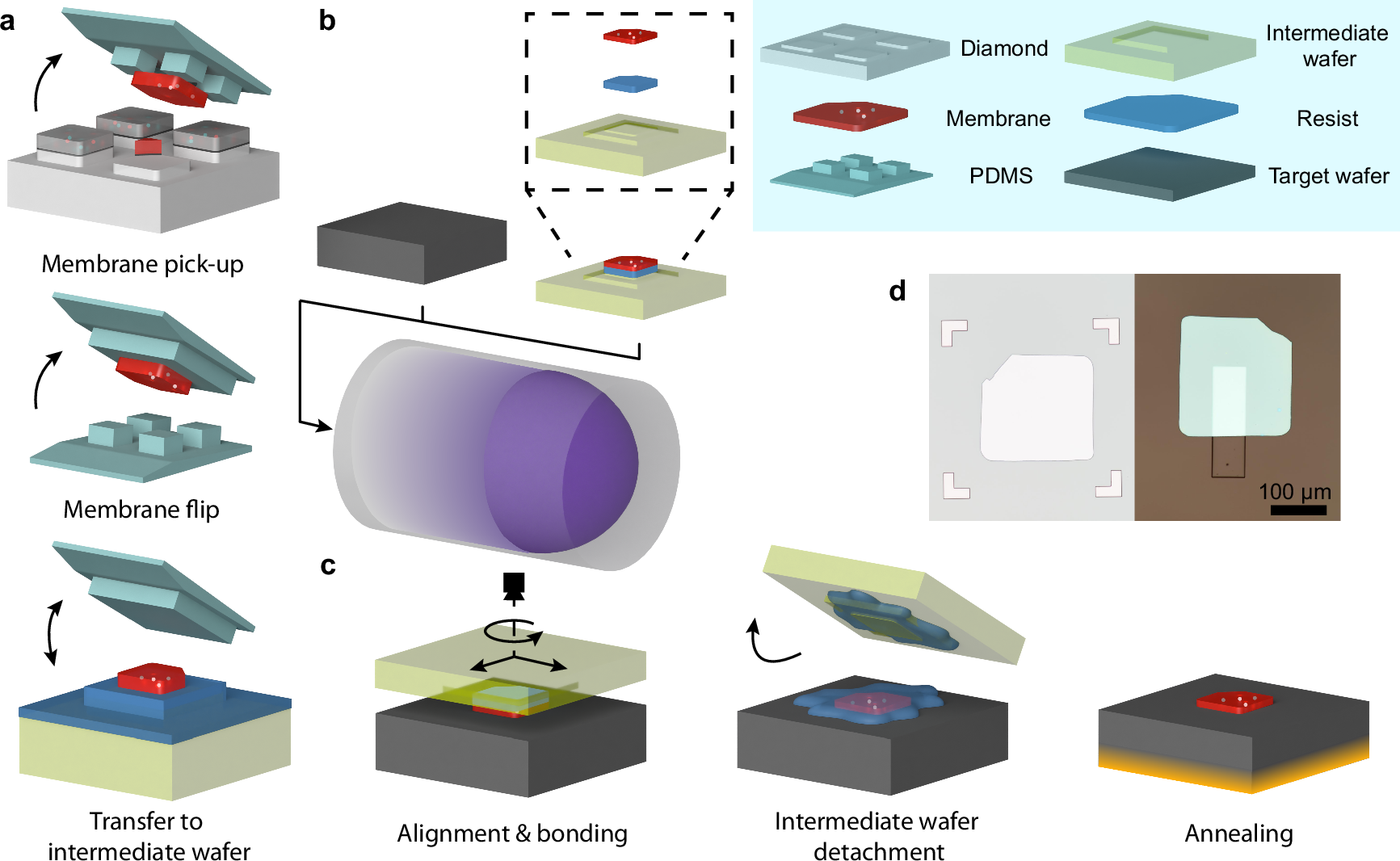
Diamond has superlative material properties for a broad range of quantum and electronic technologies. However, heteroepitaxial growth of single crystal diamond remains limited, impeding integration and evolution of diamond-based technologies. Here, we directly bond single-crystal diamond membranes to a wide variety of materials including silicon, fused silica, sapphire, thermal oxide, and lithium niobate. Our bonding process combines customized membrane synthesis, transfer, and dry surface functionalization, allowing for minimal contamination while providing pathways for near unity yield and scalability. We generate bonded crystalline membranes with thickness as low as 10 nm, sub-nm interfacial regions, and nanometer-scale thickness variability over 200 by 200 μm2 areas. We measure spin coherence times T2 for nitrogen vacancy centers in 150 nm-thick bonded membranes of up to 623 ± 21 μs, suitable for advanced quantum applications. We demonstrate multiple methods for integrating high quality factor nanophotonic cavities with the diamond heterostructures, highlighting the platform versatility in quantum photonic applications. Furthermore, we show that our ultra-thin diamond membranes are compatible with total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy, which enables interfacing coherent diamond quantum sensors with living cells while rejecting unwanted background luminescence. The processes demonstrated herein provide a full toolkit to synthesize heterogeneous diamond-based hybrid systems for quantum and electronic technologies.