2023-08-31 デューク大学(Duke)
◆この研究は、材料科学の分野で注目されているペロブスカイト材料に焦点を当てており、特に有機半導体を含む複雑な構造の材料を制御する方法を解明しました。これにより、新しい光電子デバイスの設計やエネルギー効率の向上に寄与する可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://pratt.duke.edu/about/news/growing-triple-decker-hybrid-crystals-lasers
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-023-01311-0
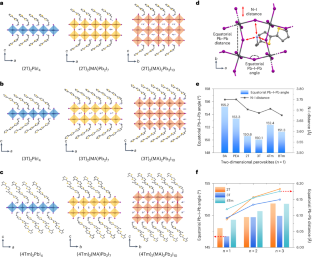
有機半導体内包ペロブスカイトの膜厚制御 Thickness control of organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites
Jee Yung Park,Ruyi Song,Jie Liang,Linrui Jin,Kang Wang,Shunran Li,Enzheng Shi,Yao Gao,Matthias Zeller,Simon J. Teat,Peijun Guo,Libai Huang,Yong Sheng Zhao,Volker Blum & Letian Dou
Nature Chemistry Published:31 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01311-0
Abstract
Two-dimensional organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskites are a promising family of hybrid materials for optoelectronic applications, owing in part to their inherent quantum well architecture. Tuning their structures and properties for specific properties, however, has remained challenging. Here we report a general method to tune the dimensionality of phase-pure organic semiconductor-incorporated perovskite single crystals during their synthesis, by judicious choice of solvent. The length of the conjugated semiconducting organic cations and the dimensionality (n value) of the inorganic layers can be manipulated at the same time. The energy band offsets and exciton dynamics at the organic–inorganic interfaces can therefore be precisely controlled. Furthermore, we show that longer and more planar π-conjugated organic cations induce a more rigid inorganic crystal lattice, which leads to suppressed exciton–phonon interactions and better optoelectronic properties as compared to conventional two-dimensional perovskites. As a demonstration, optically driven lasing behaviour with substantially lower lasing thresholds was realized.