カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校のエンジニアが、驚くべき表面上に均一なリチウム結晶を成長させ、リチウム金属電池の急速充電への新たな扉を開いた By growing uniform lithium crystals on a surprising surface, UC San Diego engineers open a new door to fast-charging lithium-metal batteries
2023-02-09 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
◆リチウム金属電池を約1時間で充電できるようになり、これは現在のリチウムイオン電池に匹敵する速度である。カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校のエンジニアは、カリフォルニア大学アーバイン校の画像処理研究者と共同で、この進歩について、2023年2月9日付の『Nature Energy』に発表しています。
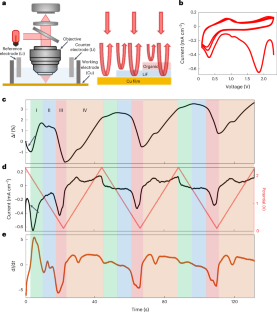
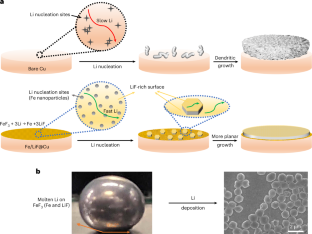
◆研究者らは、リチウム金属結晶を成長させるために、リチウム金属電池の負極側にある一般的な銅の表面を、フッ化リチウム(LiF)と鉄(Fe)からなるリチオフォビックナノコンポジット表面と置き換えた。この疎水性表面を利用してリチウムを析出させると、リチウム結晶の種ができ、その種から高密度のリチウム層が成長し、高い充電率でもリチウムを析出させることができた。その結果、急速充電が可能で長サイクル寿命のリチウム金属電池が実現した。
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/progress-toward-fast-charging-lithium-metal-batteries
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41560-023-01202-1
リチウム金属電池の急速充電を可能にするリチオフォビック基板上での単結晶シード育成。 Growing single-crystalline seeds on lithiophobic substrates to enable fast-charging lithium-metal batteries
Zhaohui Wu,Chunyang Wang,Zeyu Hui,Haodong Liu,Shen Wang,Sicen Yu,Xing Xing,John Holoubek,Qiushi Miao,Huolin L. Xin & Ping Liu
Nature Energy Published:09 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-023-01202-1
Abstract
Controlling the nucleation and growth of lithium metal is essential for realizing fast-charging batteries. Here we report the growth of single-crystalline seeds that results in the deposition of dense lithium, even at high current densities. Contrary to the widely accepted practice of using a lithiophilic surface to achieve dendrite-free deposition, we employ a lithiophobic surface made of a nanocomposite of LiF and Fe to deposit hexagonal crystals, which induce subsequent dense lithium deposition. The nanocomposites have uniform Fe sites for nucleation while LiF enables rapid lithium transport. A cell using a 3 mAh cm−2 LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 (LiNMC811) cathode, onefold excess of lithium and 3 g Ah−1 electrolyte cycles at a 1 C rate for more than 130 cycles with 80% capacity retention, a 550% improvement over the baseline cells. Our findings advance the understanding of lithium nucleation and pave the way for realizing high-energy, fast-charging Li-metal batteries.