(3D-printing technology at UD enables novel lenses for wireless communications)
2020/12/14 アメリカ合衆国・デラウェア大学 (UD)
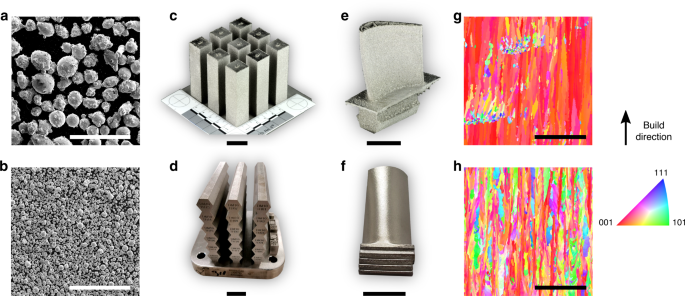
・ UD および UD Additive Manufactruing Technology Center が、3D プリンティングによるワイヤレス通信用の屈折率分布型(GRIN)ルーネベルグ・レンズアンテナの作製技術を開発。
・ プラスチック製の同 GRIN レンズは、光学レンズとは異なり、携帯電話や 5G 技術の周波数で作動して通信信号を特定の方向へと変換できる。このようなレンズ機能はワイヤレス通信で切望されていたが、実現が困難であった。
・ 積層造形技術(AM)である 3D プリンティング技術は、低コストでより高速な製品のカスタム化を実現しながら、廃棄物の排出量を従来方法よりも低減する。
・ 同 3D プリンティング技術では、極めて微小なスケールでプラスチックを調節し、レンズの各箇所で材料特製を変化させることができる。レンズ上の正確な場所への電磁特性のカスタム配置が可能なパターンに 3D 構造を作製する。
・ また、レンズ底部面が平坦な設計で、電子機器、センサーやバッテリー等の機能の追加が可能なため、微小なアンテナを備えた携帯電話技術のようなアプリケーションへの統合も可能。
・ 同 GRIN レンズは低コストで頑丈なため、ネットワークの末端に取り付けて自動運転車との相互通信や、レーダーによる障害物自動回避等の「エッジ・オブ・ネットワーク」的なアプリケーションでの有用性が期待できると考える。
・ 同 GRIN レンズの実装に向け、AM 技術による防衛、電気通信および製薬アプリケーション用の製品開発を専門とする地元のスタートアップ企業の DeLUX Advanced Manufacturing と共同で開発を進める。
・ AM 技術研究の多くでは、従来製品の代替を目的とした金属やプラスチックによる構造体の作製が中心となっているが、UD Center では、完全な電子レーザーシステムや通信システムを人間の関与無く製造する、AM プロセスにエレクトロニクスやエネルギーシステムを統合したスマート材料開発に重点的に取り組んでいる。
・ 長期的な目標には、3D プリント完了後にベルトコンベアから自動で立ち上がり、次のロボット製造開始のボタンを押してから移動する完全自律型ロボットの開発も含む。現時点では、プリントヘッドから近くのテーブルへと自律移動する 3D プリントオブジェクトの開発に成功している。
・ 本研究は米国陸軍との共同プロジェクト。米国国防総省が資金を提供した。
URL: https://www.udel.edu/udaily/2020/december/mirotznik-3d–printing-lens-technology/
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
(関連情報)
Scientific Reports 掲載論文(フルテキスト)
High gain, wide-angle QCTO-enabled modified Luneburg lens antenna with broadband anti-reflective
layer
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-69631-6
Abstract
The gradient-index (GRIN) Luneburg lens antenna offers significant benefits, e.g. high aperture efficiency, low-power, minimal cost, wide beam scanning angle and broad bandwidth, over phased array antennas and reflector antennas. However, the spherical shape of the Luneburg lens geometry complicates the integration of standard planar feed sources and poses significant implementation challenge. To eliminate the feed mismatch problem, the quasi-conformal transformation optics (QCTO) method can be adopted to modify the lens’ spherical feed surface into a planar one. However, Luneburg lenses designed with QCTO method are limited to poor performance due to the presence of the reflections and beam broadening arising from the quasi-conformal mapping. In this paper, we present a new method of implementing QCTO-enabled modified Luneburg lens antenna by designing a broadband anti-reflective layer along with the modified lens’s planar excitation surface. The proposed anti-reflector layer is inherently broadband in nature, has a continuously tapered inhomogeneous dielectric permittivity profile along its thickness, and ensures broadband impedance matching. To show the new QCTO modified Luneburg lens antenna, an example lens antenna was designed at Ka-band (26–40 GHz) and fabricated using fused deposition modeling (FDM) based additive manufacturing technique. Electromagnetic performance of the lens antenna was experimentally demonstrated.