(A miniature stretchable pump for the next generation of soft robots)
2019/8/14 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL) (ローザンヌ工科大学)


・ EPFL が芝浦工業大学および電気通信大学と共同で、フレキシブルで静音、超軽量の伸縮性ソフトポンプを開発。
・ 機械の可動部に流し込んだ液体で駆動する、騒音を出す固くかさばる従来のポンプの代替として、ソフトロボットや軽量なパワードスーツ、スマートな衣類等での利用が期待できる。
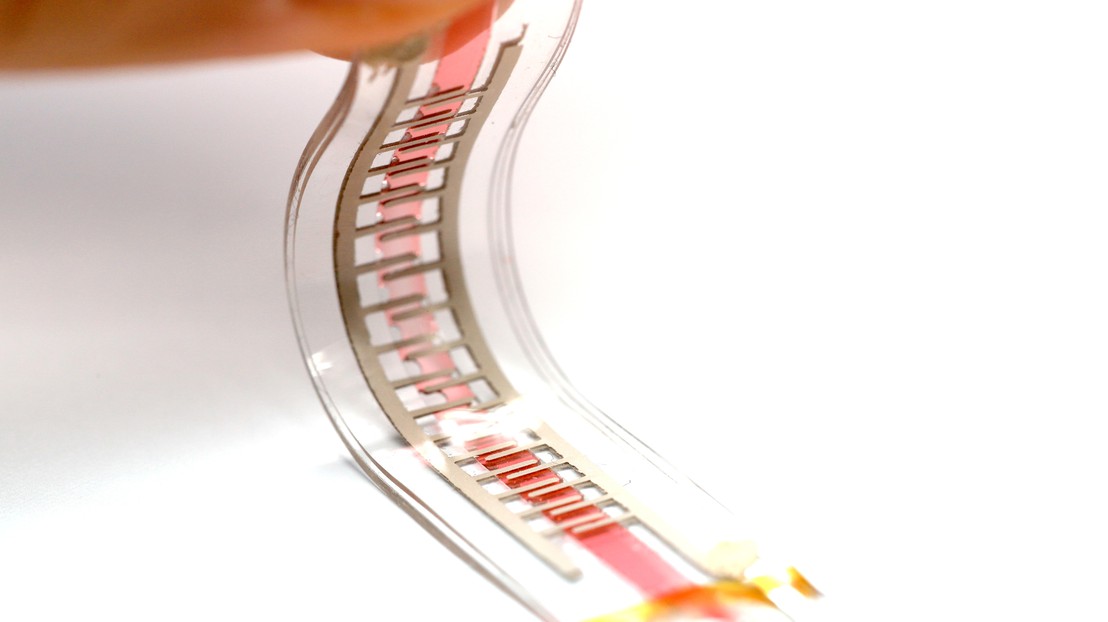
・ 新開発のソフトポンプは、電極もフレキシブルで僅か 1g と超軽量。充電池を含む 2cm 四方の回路が供給する電力のみで駆動する。同ポンプを複数接続することで、大型のロボットのアクチュエーションも可能。
・ スーパーコンピューターのようなシステム内で冷却液を循環させるメカニズムをベースとした同ソフトポンプは、チューブ形状の直径 1mm の流路とその内部にプリントした電極の列より構成される。
・ ポンプを満たす誘電性の液体に電圧を加えると、電極から電子が放出され、液体中の分子に電荷を付与する。これらの分子が別の電極に引き付けられることに伴って液体がチューブ内を移動。電場を調整することで、静音を維持したまま、液体が流れる速度を上げることもできる。
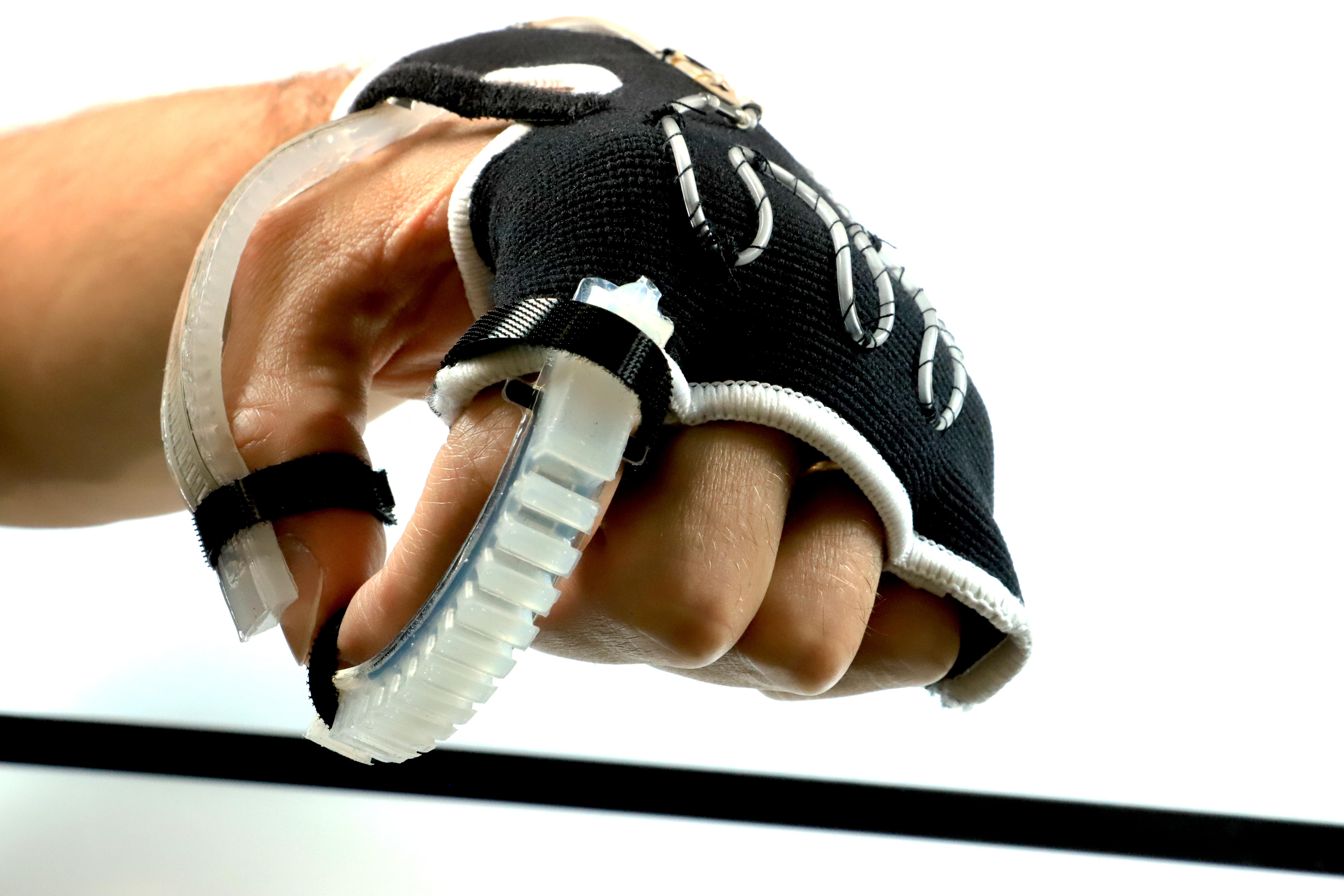
・ ソフトロボットの研究室で使用されているロボットフィンガーに同ポンプを埋め込むことに成功。液体駆動型人工筋肉とフレキシブルなパワードスーツを開発する、鈴森・遠藤研究室との共同研究を進める。
・ また、同ポンプを布製のグローブに取付けることで、グローブの任意の箇所の冷暖房を実証。このアプリケーションには複数の企業が関心を寄せている。
・ 本研究の資金は、日本学術振興会(JSPS)科研費、文科省(MEXT)/JSPS の卓越研究員事業、スイス国立コンピテンスセンター・ロボティクス研究所(NCCR Robotics)を通じスイス国立科学財団 (SNSF)、トビタテ!留学 JAPAN 日本代表プログラムおよび Hasler Foundation Cyber-Human Systems program が提供した。
URL: https://actu.epfl.ch/news/a-miniature-stretchable-pump-for-the-next-generati/
(関連情報)
Nature 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料) Stretchable pumps for soft machines URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1479-6
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
Abstract
Machines made of soft materials bridge life sciences and engineering. Advances in soft materials have led to skin-like sensors and muscle-like actuators for soft robots and wearable devices. Flexible or stretchable counterparts of most key mechatronic components have been developed, principally using fluidically driven systems other reported mechanisms include electrostatic stimuli-responsive gels and thermally responsive materials such as liquid metals and shape-memory polymers. Despite the widespread use of fluidic actuation, there have been few soft counterparts of pumps or compressors, limiting the portability and autonomy of soft machines. Here we describe a class of soft-matter bidirectional pumps based on charge-injection electrohydrodynamics. These solid-state pumps are flexible, stretchable, modular, scalable, quiet and rapid. By integrating the pump into a glove, we demonstrate wearable active thermal management. Embedding the pump in an inflatable structure produces a self-contained fluidic ‘muscle’. The stretchable pumps have potential uses in wearable laboratory-on-a-chip and microfluidic sensors, thermally active clothing and autonomous soft robots.